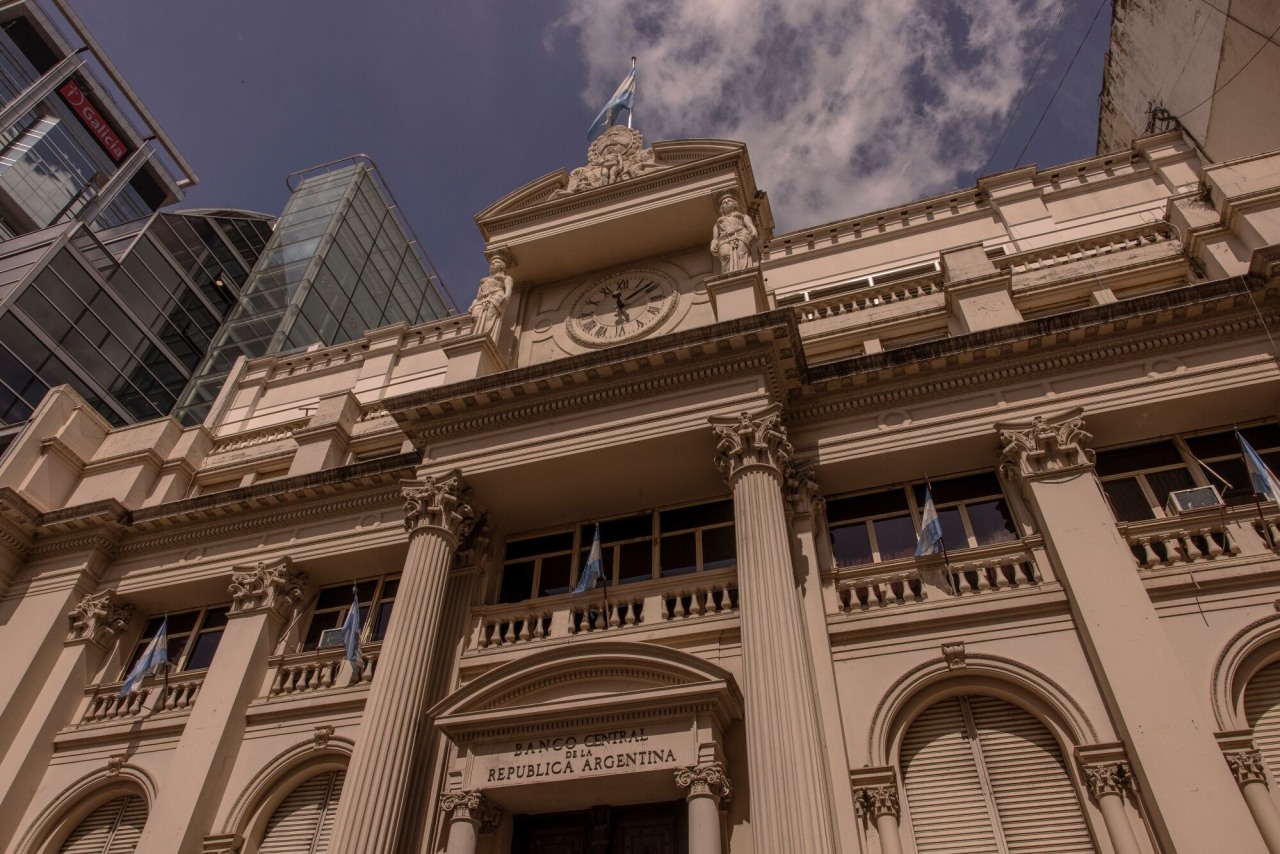
The Central Bank of Argentina announced plans to modify its currency band in a bid to address the overvaluation of the Argentine peso and bolster international reserves. This decision, made under the leadership of President Javier Milei, marks a significant shift in the country’s monetary policy as it seeks to stabilize its economy.
The adjustments to the currency band aim to enhance the competitiveness of Argentine exports while managing inflation, which has plagued the nation for years. With the peso struggling against the US dollar, the central bank believes that a more flexible exchange rate will allow for better alignment with market realities.
As of October 2023, the official exchange rate of the Argentine peso stands at approximately 350 ARS to 1 USD. In comparison, the unofficial rate has soared well above 700 ARS, illustrating the disparity that has developed in the country’s currency market. By changing the currency band, the Central Bank of Argentina hopes to narrow this gap, ultimately restoring confidence among investors and consumers alike.
President Milei’s administration is focused on rebuilding international reserves, which have dwindled significantly in recent years. The central bank’s strategy includes attracting foreign investment and implementing policies that encourage export growth. This approach is crucial for a country that has faced numerous economic challenges, including high inflation rates, which reached over 100% annually in 2023.
In a recent statement, the central bank emphasized the importance of these changes, noting that they are designed to create a more predictable and stable economic environment. “We must take decisive action to ensure that our currency reflects its true value and to support our international reserves,” the bank stated.
The move has drawn mixed reactions from economists and market analysts. Some view it as a necessary step towards economic recovery, while others remain cautious about the potential risks associated with a more flexible exchange rate. The success of this policy will largely depend on the government’s ability to implement complementary measures that address inflation and restore public trust in the financial system.
Argentina’s economic situation remains precarious, with many citizens experiencing the direct impact of inflation on their daily lives. The government’s commitment to reforming the currency system reflects an understanding of the urgency required to improve economic stability and foster growth.
As the situation develops, observers will be closely monitoring the impact of these changes on the Argentine peso, investor confidence, and the broader economic landscape. The government’s actions in the coming months will be critical in shaping the future trajectory of Argentina’s economy, as it seeks to recover from years of turbulence.