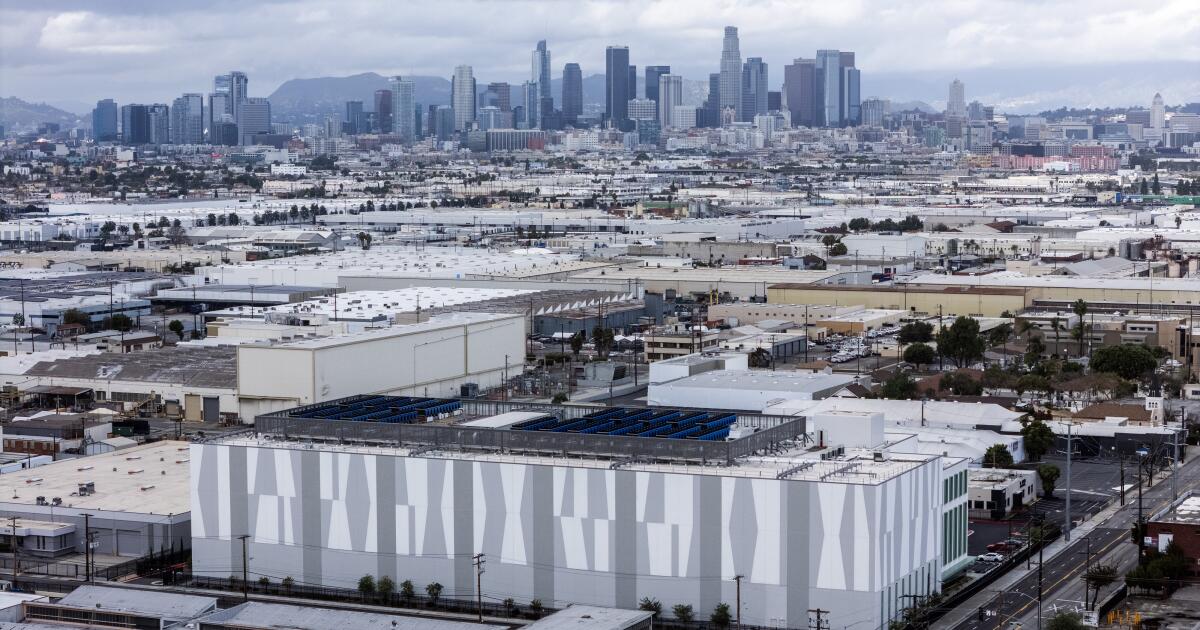
Just five miles south of downtown Los Angeles, the small industrial city of Vernon is transforming into a critical hub for artificial intelligence infrastructure. The city, home to just over 200 residents, hosts a three-story, 242,000-square-foot data center known as LAX01. This facility is consuming enough electricity to power more than 26,400 homes for an entire year, signaling a rapid shift in the region’s industrial landscape.
Vernon has a storied history marked by corruption scandals and environmental issues. Once on the verge of being unincorporated due to accusations of control by a few families, the city has recently gained attention for its burgeoning role in the AI sector. “The race toward superintelligence is reshaping infrastructure requirements across every industry,” said Michael Wall, executive vice president at Prime Data Centers, which developed the LAX01 facility. “We’re working to give businesses the foundation they need to build and deploy the next generation of AI models — faster, more efficiently and at massive scale.”
Investment Surge and Infrastructure Growth
The data center boom in Vernon is part of a larger trend across the United States. According to Goldman Sachs, tech giants like Google, Amazon, Microsoft, and Meta invested approximately $465 billion in computing and networking infrastructure for AI in 2025. Such investments are crucial, as a Harvard economist indicated that without them, the country’s gross domestic product growth could have nearly stagnated this year.
Vernon’s appeal lies not only in its industrial legacy but also in its relatively low operational costs compared to other Southern California locales. The city operates its own publicly owned utility, providing electricity, water, gas, and fiber-optic internet. This allows Vernon to offer excess power capacity at rates that can be as low as half of those charged by other providers in the region.
Developers like Goodman Group, CoreSite, and Digital Realty are planning to add hundreds of megawatts of new data center capacity in Vernon, according to Darren Eades, managing director of JLL, who specializes in data centers. He noted that the recent surge in data center development is primarily driven by the demand for AI technologies.
Challenges and Community Response
Despite the promising developments, challenges remain. Communities across the U.S. have often opposed new data center projects due to concerns about resource consumption and environmental impact. In California, local legislation restricts projects to 49.9 megawatts of power to avoid extensive regulatory requirements. This limitation has influenced the design and scale of Vernon’s new data centers.
Vernon has not faced significant opposition to its data center initiatives. A spokesperson for the city noted that there have been no objections from the community regarding the new developments. The city provided a frequently asked questions document stating that the increase in electrical load and water demand will not necessitate additional purchases, a common concern in other jurisdictions that leads to rate increases.
Despite the optimistic outlook, analysts caution that the growing demand for power, coupled with the rising costs of infrastructure, could eventually impact electricity rates. California is already the third-largest data center hub in the United States, trailing only Texas and Virginia. A Bloomberg analysis indicated that electricity costs have surged by as much as 267% in areas near data centers over the past five years.
As companies continue to invest in AI, the infrastructure in Vernon may soon face its limits. “We didn’t use to speak in megawatts when we thought of data centers; we used to think in terms of just kilowatts,” said Robert Brooks, vice president of sales at Lambda, a cloud computing firm that has leased a majority of the LAX01 data center.
Vernon’s evolution from a struggling industrial town to a vital player in the AI data center landscape illustrates the shifting dynamics of technology and infrastructure. As demand for AI capabilities continues to grow, the city’s role will likely expand, shaping not only its future but also the broader technological landscape in Southern California.