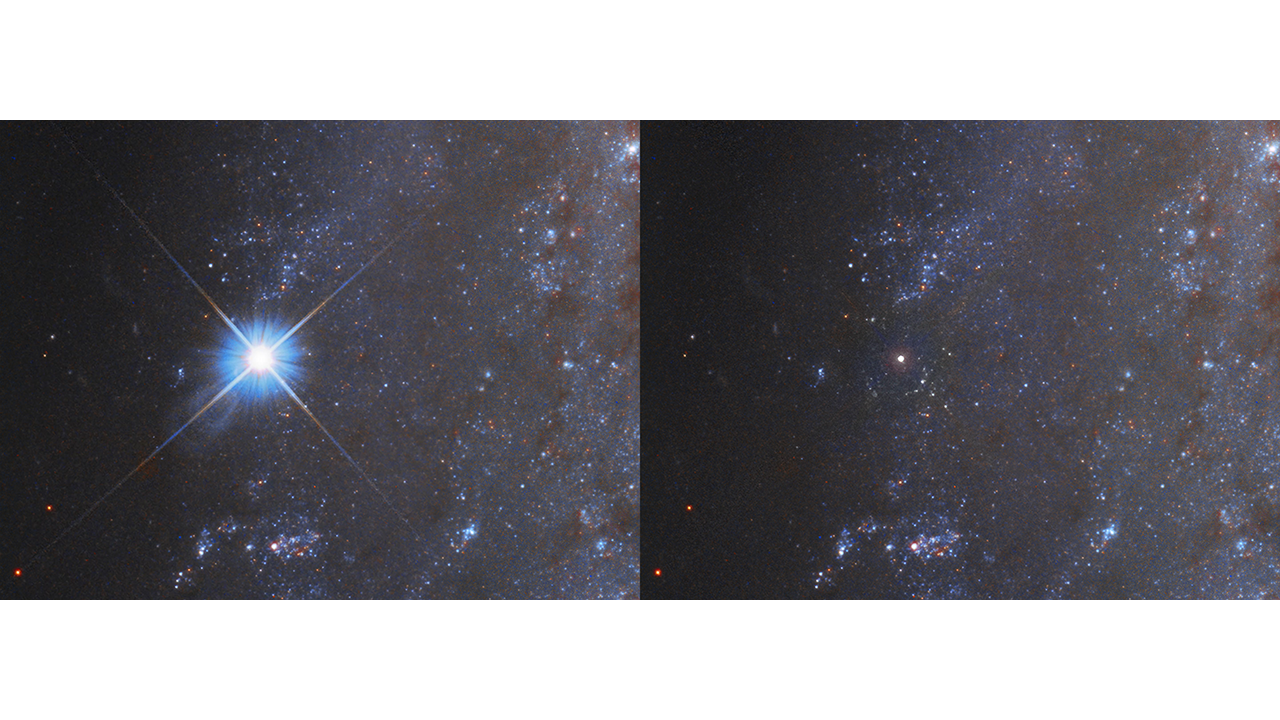
BREAKING: NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has just revealed an extraordinary before-and-after view of the supernova explosion known as SN 2018gv, captured in stunning detail. This remarkable event, located in the spiral galaxy NGC 2525, is approximately 70 million light-years away from Earth and highlights the dramatic brightness fluctuations of supernovae.
The newly released images show a striking contrast in brightness over a year, illustrating how SN 2018gv has faded since it was first detected by amateur astronomer Koichi Itagaki in early 2018. Hubble’s observations are crucial for understanding these cosmic phenomena, which are classified as Type Ia supernovae. These stellar explosions are known as “standard candles” due to their consistent peak brightness, allowing astronomers to calculate distances across the universe with remarkable accuracy.
This supernova’s significance extends beyond mere aesthetics; it plays a vital role in studying the expansion rate of the universe. Astronomers utilize SN 2018gv to analyze how this rate has changed over time, deepening our understanding of cosmic evolution. The upcoming Nasa’s Roman Space Telescope, currently under construction, aims to further investigate such explosions, promising to enhance our knowledge of the universe’s expansion.
As of August 22, 2025, the public can view these captivating images and engage with the ongoing research about supernovae and the cosmos. The findings not only appeal to astronomy enthusiasts but also invoke a sense of wonder about the universe’s vastness and our place within it.
Stay updated on the latest developments in space exploration and discoveries by following NASA’s official channels. The revelations from the Hubble Space Telescope continue to inspire curiosity and excitement about the universe, making this a pivotal moment in astronomical research.
Want to dive deeper into the mysteries of the universe? Check out NASA’s resources on the Hubble Space Telescope and its groundbreaking contributions to our understanding of space.