Smart glasses have transitioned from science fiction to a reality that offers hands-free video recording capabilities. These innovative devices feature cameras embedded directly into eyewear, allowing users to capture experiences without the interruption of pulling out a smartphone. This advancement opens new avenues for documenting life in a manner that feels more spontaneous and genuine.
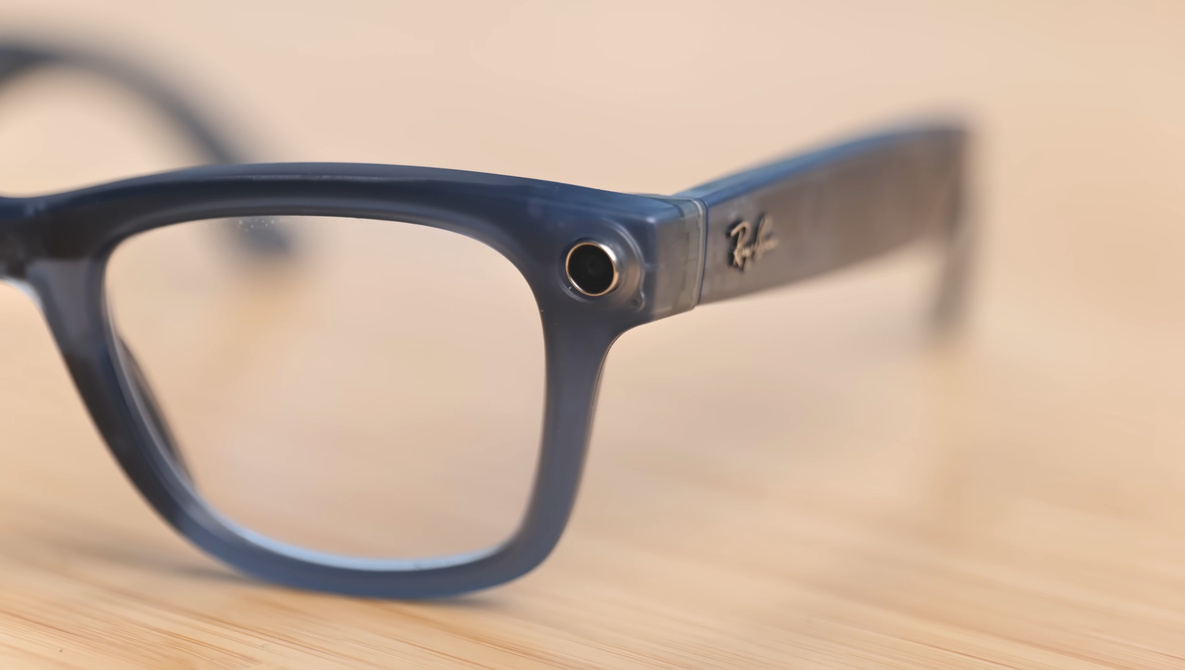
In a recent review, content creator James Warner explored the practicalities and limitations of these smart glasses. The devices are equipped with a 12-megapixel wide-angle camera, which, while decent on paper, produces images reminiscent of smartphone technology from several years ago. The video quality reaches a maximum of 1440p, and recording is capped at three minutes per clip. Although the results are suitable for casual photography, they fall short in terms of sharpness and dynamic range.
Practicality Meets Limitations
Warner highlights the advantages of shooting from a first-person perspective, noting that this feature can be particularly useful in various scenarios. For example, recording while biking or capturing candid moments with family becomes more seamless when using smart glasses. He even developed a magnetic lens adapter, allowing for the use of inexpensive smartphone lenses to expand the glasses’ capabilities.
Despite these advantages, Warner addresses several frustrations that come with the technology. Users often experience lag when triggering shots, and the battery life can be disappointingly short. Additionally, the requirement to use a specific app limits the user experience to Meta’s ecosystem, which may deter potential buyers.
The ability to document moments while remaining engaged in the activity is a significant selling point. Unlike holding a phone, wearing a camera allows for a more immersive experience. However, this practical aspect is counterbalanced by limitations that users must consider.
Privacy Concerns and Social Acceptance
The introduction of smart glasses into daily life raises important privacy questions. Having a camera on one’s face can evoke the discomfort many experienced when smartphones became ubiquitous. Although the glasses feature an indicator light that alerts others when recording, Warner points out that this measure does not fully address privacy concerns. He admits he would hesitate to wear them in sensitive environments, such as classrooms or restrooms, suggesting that societal norms have yet to adapt to this new technology.
Warner’s review emphasizes that the conversation surrounding smart glasses extends beyond technical specifications. It delves into how these devices integrate into everyday life, highlighting the ongoing tension between innovation and social acceptance.
For a comprehensive overview of the capabilities and limitations of smart glasses, viewers can check out Warner’s full video review. This exploration of wearable technology offers valuable insights for anyone considering adopting this new way to capture their experiences.
In the realm of photography, Alex Cooke, a Cleveland-based photographer and meteorologist, encapsulates the excitement that these advancements bring while also acknowledging the challenges they pose. As the world continues to embrace technologies that enhance daily life, the discussion around smart glasses remains relevant, reflecting broader themes of innovation and privacy in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.