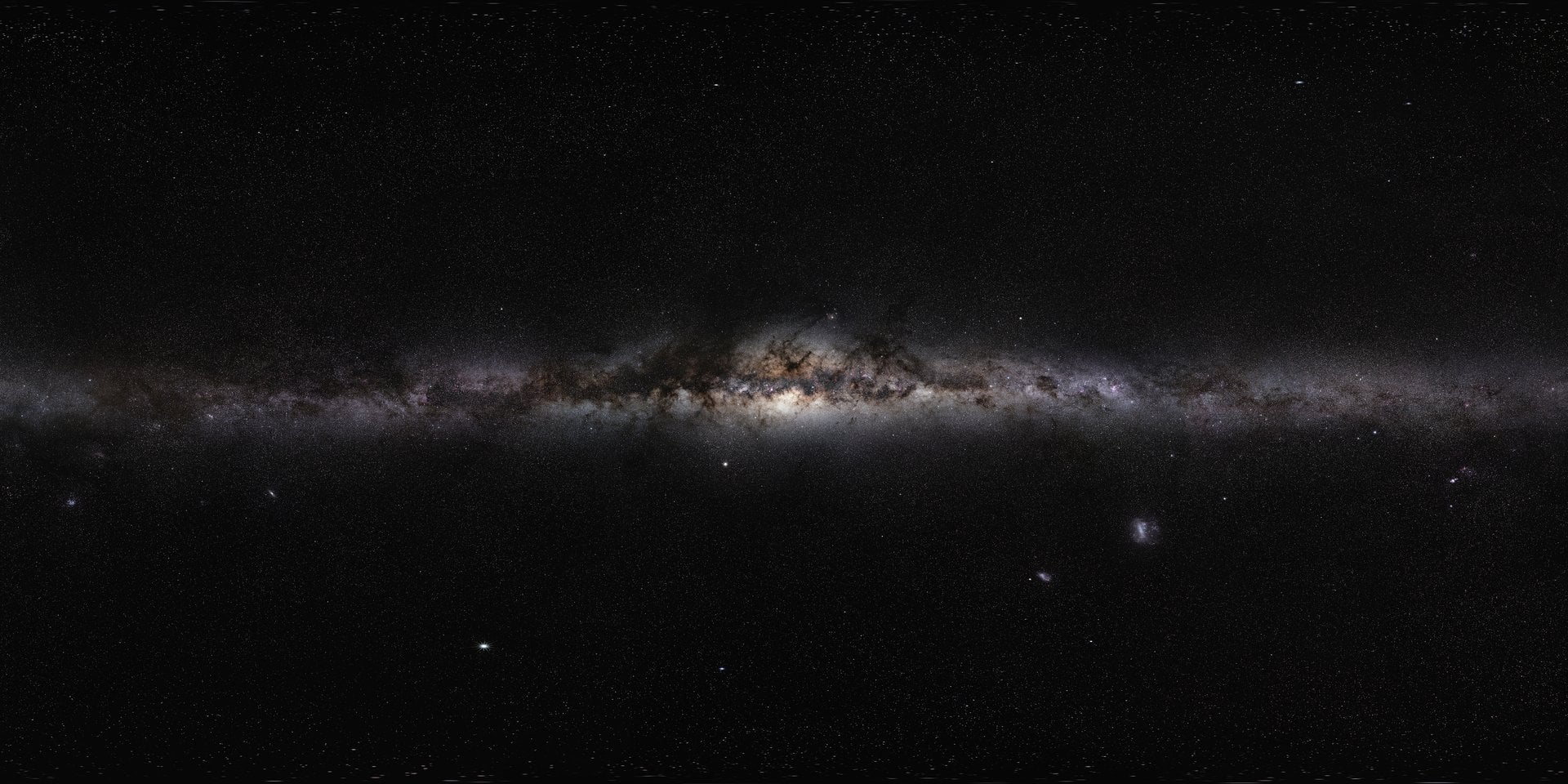
Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Interdisciplinary Theoretical and Mathematical Sciences (iTHEMS) in Japan, in collaboration with the University of Tokyo and the Universitat de Barcelona, have achieved a significant breakthrough in astrophysics by successfully simulating the Milky Way galaxy. This unprecedented simulation accurately represents over 100 billion stars across a timespan of 10,000 years, surpassing previous models by a factor of 100 in both detail and speed.
The innovative simulation was developed using a combination of 7 million CPU cores, advanced machine learning algorithms, and sophisticated numerical simulations. The research team presented their findings in a paper titled “The First Star-by-star N-body/Hydrodynamics Simulation of Our Galaxy Coupling with a Surrogate Model,” published in the *Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis* (SC ’25).
Revolutionizing Galactic Simulations
Previous simulations of the Milky Way have faced limitations in accurately capturing the complex dynamics of individual stars. Traditionally, models have been constrained by the computational power available, which restricted simulations to around one billion solar masses—less than 1% of the Milky Way’s total stellar population. Additionally, simulating 1 million years of galactic evolution would take over 315 hours, or more than 13 days, using state-of-the-art supercomputers.
To overcome these challenges, lead researcher Hirashima and his team implemented an AI-driven approach that utilizes a machine learning surrogate model. This innovative model was trained on high-resolution simulations of supernovae, allowing it to predict the influence of these explosive events on surrounding gas and dust over a period of 100,000 years following an explosion. The combination of this AI model with traditional physical simulations enabled the team to analyze both the large-scale dynamics of the galaxy and small-scale stellar phenomena simultaneously.
Time and Energy Efficiency
The team rigorously tested their simulation model on the Fugaku and Miyabi Supercomputer Systems at RIKEN and the University of Tokyo, respectively. The results were remarkable: the new method could simulate a million years of galactic evolution in just 2.78 hours. This efficiency means that a complete simulation of 1 billion years of galactic history could be achieved in approximately 115 days.
These advancements provide astronomers with a robust tool for examining theories regarding galactic evolution and the formation of the universe. The incorporation of surrogate AI models not only reduces the time and energy required for complex simulations but also opens up possibilities for similar methodologies in other scientific fields. Areas such as meteorology, ocean dynamics, and climate science could benefit from this approach, enhancing our understanding of various natural phenomena.
The implications of this research extend far beyond the realm of astrophysics. By pushing the boundaries of computational capabilities, the RIKEN team has paved the way for future explorations that could reshape our understanding of the universe and the forces that govern it. As Hirashima noted in a recent press release, the potential applications of this technology could transform numerous scientific disciplines, ushering in a new era of research and discovery.