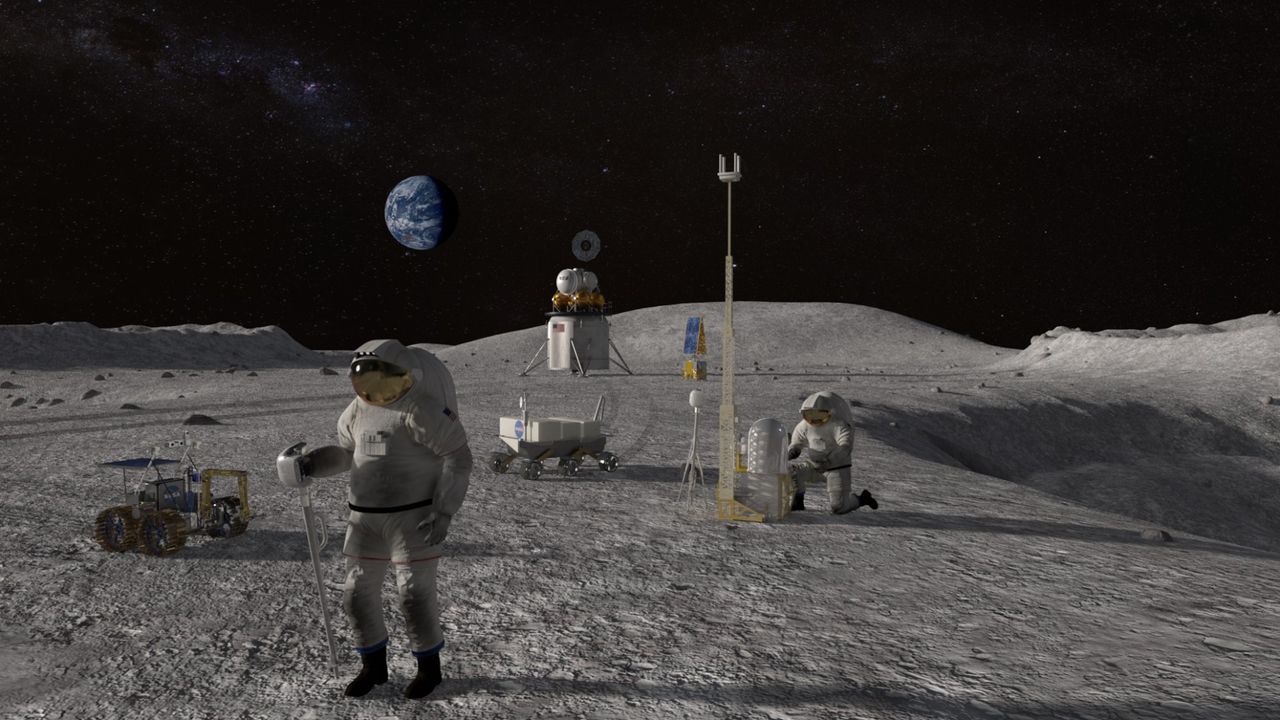
NASA and Google have initiated a collaboration to test an AI-powered medical assistant intended for use by astronauts on long-duration missions. This innovative technology aims to address the challenges posed by communication delays with Earth, which can make real-time medical consultations impractical during missions to the moon and Mars.
The project centers around a proof of concept for a system known as the Crew Medical Officer Digital Assistant (CMO-DA), which falls under the category of Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS). By equipping astronauts with this digital assistant, NASA seeks to empower them to autonomously diagnose and treat symptoms while operating beyond low Earth orbit.
According to a statement from Google on August 8, 2023, the AI system is designed to analyze crew health and performance efficiently. It has been trained on extensive spaceflight literature, utilizing advanced natural language processing and machine learning techniques. Early results suggest that the AI may provide reliable diagnoses based on reported symptoms, demonstrating its potential utility in critical situations.
Addressing Communication Delays
Deep-space missions often encounter communication delays, particularly when traveling to Mars, where signals can take up to 45 minutes to make a round trip. This limitation underlines the necessity for an onboard medical support system, as immediate consultations with Earth-based medical professionals become impossible. A swift return to Earth is also not an option for astronauts facing urgent health issues.
The introduction of an AI assistant could significantly enhance medical care in these scenarios, bridging a crucial gap in astronaut health management. Moreover, the technology developed for space missions has potential applications in remote and underserved areas on Earth, where access to qualified medical personnel is limited.
NASA and Google are currently collaborating with medical professionals to refine and further test the CMO-DA model, ensuring that it meets the unique needs of astronauts during their missions. This development aligns with NASA’s commitment to advancing human spaceflight through its Artemis program, which aims to establish a sustainable human presence on the moon and eventually facilitate missions to Mars.
As this partnership progresses, both organizations look forward to exploring the broader implications of AI in healthcare, both in space and on Earth. The potential for AI to revolutionize medical support in challenging environments could lead to significant advancements in how health care is delivered, regardless of location.