The Hayli Gubbi volcano in Northern Ethiopia erupted on November 23, 2025, marking its first eruption in nearly 12,000 years. This significant geological event has disrupted nearby villages, covering them in a thick layer of ash and affecting both homes and livestock.
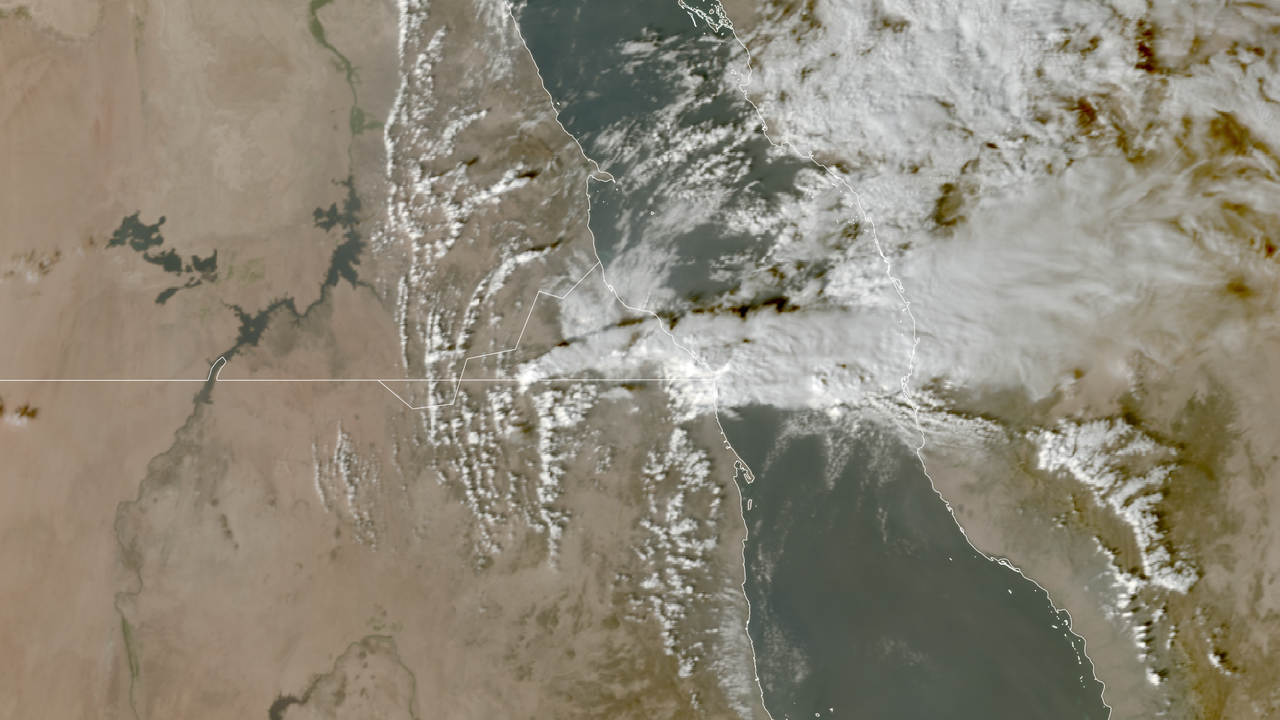
Satellite imagery from the European Space Agency depicted extensive ash plumes rising approximately 8.7 miles (14 kilometers) into the atmosphere, impacting air travel as far away as Pakistan and Northern India. Flights were canceled for several days during the week, and the ash is now reportedly moving toward China.
Community Response and Health Concerns
Fortunately, no casualties have been reported from the eruption. However, local health officials are taking precautionary measures. Abedella Mussa, a health official from the Afdera district, confirmed that mobile medical services were dispatched from the Afar region to assist the affected neighborhoods, known locally as kebeles. The swift response aims to address potential health issues arising from ash exposure and ensure the well-being of residents.
The last known eruption of Hayli Gubbi coincided with the beginning of the Holocene Epoch, a period characterized by significant climatic changes following the last ice age, which ended approximately 2.6 million years ago.
Seismologist and researcher Atalay Ayele from the Institute of Geophysics, Space Science and Astronomy at Addis Ababa University, noted that Ethiopia is home to around 50 active volcanoes. He stated, “At any time, these volcanoes can be active or can show manifestations of activity.” Despite no scientific forecasts predicting this eruption, locals had observed minor smoke emissions from Hayli Gubbi in the days leading up to the eruption.
Historical Context and Regional Volcanic Activity
The eruption of Hayli Gubbi is not the only volcanic activity Ethiopia has faced in recent months. Earlier in July 2025, the Erta Ale volcano, known for its persistent lava lake, also produced a dense black cloud, indicating continued geological unrest in the region.
As of November 28, 2025, reports indicate that the activity at Hayli Gubbi has ceased. Authorities continue to monitor the situation closely, given the potential for further eruptions from this and other nearby volcanoes. The community remains vigilant, and ongoing assessments are crucial to ensure the safety and health of those affected by this remarkable geological event.