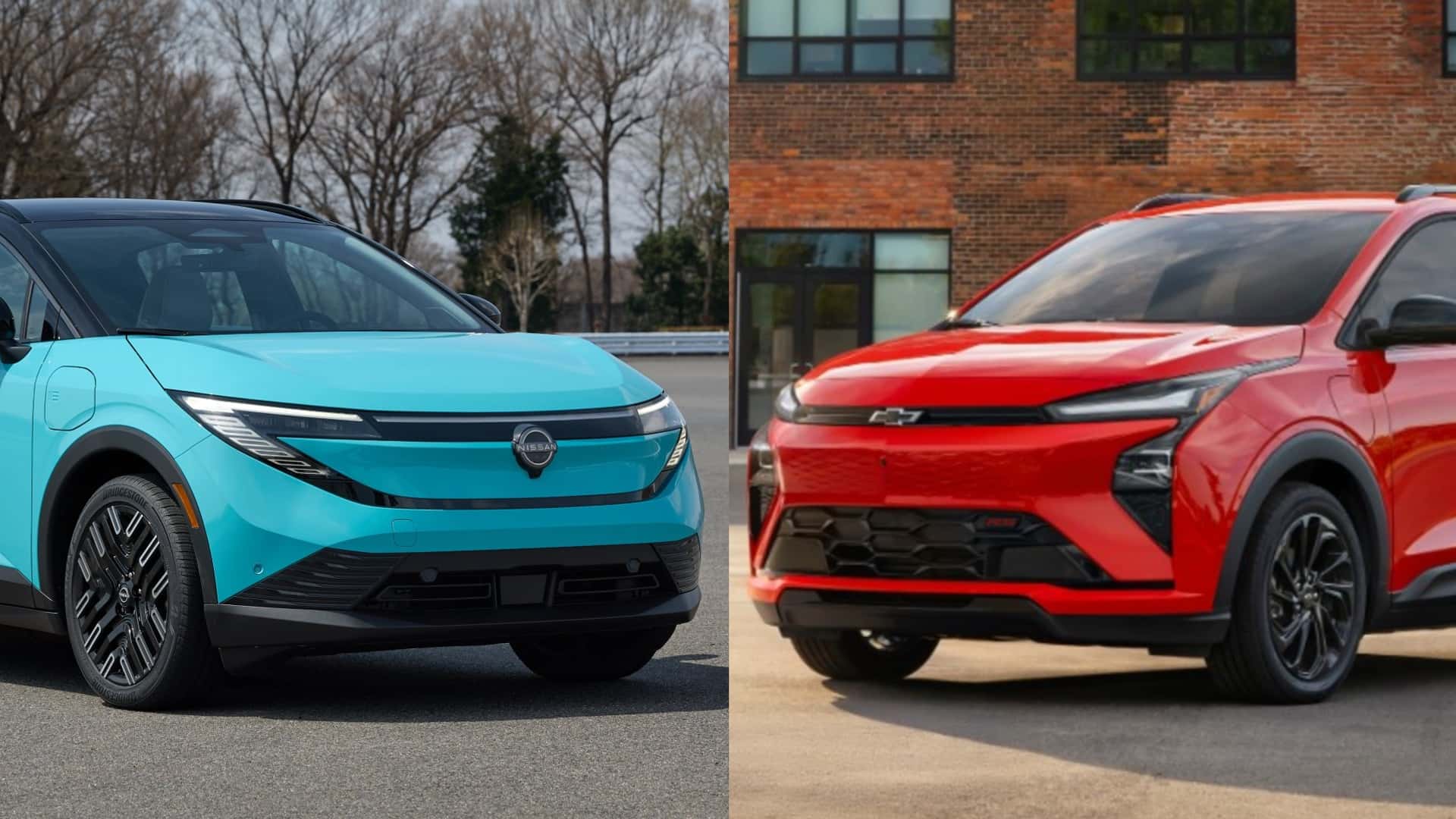
The electric vehicle landscape in the United States is evolving with the introduction of the 2027 Chevrolet Bolt and the 2026 Nissan Leaf. Both models are positioned as affordable options, starting around $30,000, making them the most budget-friendly electric vehicles available. While the Bolt is set to launch at a price of $29,990, the Leaf’s starting price is $31,485. This price point is significant, especially as the market adjusts in the wake of the recently expired EV tax credit.
Pricing and Availability
The 2027 Chevrolet Bolt will be available in early 2026, with a base LT model expected to arrive shortly after at $28,995. The Nissan Leaf is already available at dealerships across the country. Notably, the Leaf will soon introduce an even more economical version, the Leaf S, which will feature a smaller battery and reduced driving range, likely undercutting the base Bolt’s price. Until then, the new Bolt holds the title of America’s most affordable battery-powered vehicle.
Design and Features
When examining the design, the Leaf has undergone a significant overhaul, being built on an entirely new platform. This redesign provides enhancements in driving range, power, and charging speed, making it a more attractive option than its predecessor. In contrast, the Bolt retains much of the body style of the previous model, although General Motors has made notable improvements to its battery and motor performance.
Both vehicles are equipped with a North American Charging Standard (NACS) port, allowing them to utilize Tesla Superchargers directly. However, the Leaf features a unique dual-port system that includes a separate J1772 port for Level 1 and Level 2 charging. The Bolt offers vehicle-to-home (V2H) capabilities, allowing it to power a home when properly set up, while the Leaf has vehicle-to-load (V2L) functionality to power tools and appliances.
Charging capabilities are competitive, with both models supporting a peak DC fast-charging rate of 150 kilowatts. The Leaf can accept 7.2 kilowatts from an AC charger, while the Bolt’s onboard AC charger can handle up to 11.5 kW. This gives the Bolt a slight advantage in charging performance.
Range, Power, and Interior
Range varies significantly between the two vehicles. The Leaf S+ boasts a driving range of 303 miles on a full charge, powered by a 75-kilowatt-hour battery. Nissan states that charging from 10% to 80% takes approximately 35 minutes. In contrast, the 2027 Bolt, with a 65 kWh lithium iron phosphate battery, offers an estimated range of 255 miles, with a quicker charging time of 26 minutes for the same percentage increase.
In terms of power, both vehicles are comparable, with the Bolt producing 210 horsepower and the Leaf slightly ahead with 214 horsepower. However, the Leaf has a significant advantage in torque, generating 261 lb-ft compared to the Bolt’s 169 lb-ft. Weight is also a factor, with the Bolt being lighter at 3,766 pounds versus the Leaf’s 4,206 pounds in its base trim.
Interior features show a divergence in technology. The Bolt is equipped with an 11-inch digital display and an 11.3-inch infotainment screen, but it lacks integration for Apple CarPlay and Android Auto. The Leaf, on the other hand, features two 12.3-inch displays in the S+ model, along with wireless support for Apple CarPlay and Android Auto, which could influence buyer preference significantly.
Safety technology also varies between the models. The Leaf comes standard with Nissan’s Safety Shield 360 Suite, which includes advanced features such as Automatic Emergency Braking and Lane Departure Prevention. The Bolt offers similar safety features, including Adaptive Cruise Control and Front Pedestrian Braking, but lacks some of the advanced monitoring systems present in the Leaf.
Both the 2027 Chevrolet Bolt and the 2026 Nissan Leaf present compelling options for consumers seeking affordable electric vehicles. While the Leaf excels in driving range and technological features, the Bolt offers a lower entry price and slightly more passenger space. Ultimately, the decision may come down to personal preferences and needs as both models prepare to compete in an increasingly crowded market.