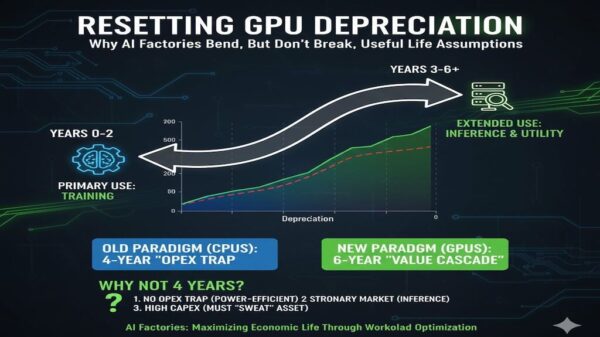
The artificial intelligence (AI) sector is undergoing significant transformation as major companies increasingly merge operations and form strategic partnerships. This shift was highlighted by OpenAI’s recent agreement to invest “tens of billions of dollars” in AMD, which includes purchasing substantial quantities of AMD microprocessors and acquiring up to a 10% stake in the semiconductor company.
Corporate Entanglements and Strategic Alliances
The landscape of AI and its supporting infrastructure is becoming indistinct, with leading firms both competing and collaborating in unprecedented ways. OpenAI CEO Sam Altman described this evolution as a necessary phase for the industry, stating, “We are in a phase of the build-out where the entire industry has got to come together.” As part of this cooperative spirit, OpenAI is also set to benefit from substantial investments from Nvidia, which plans to invest up to $100 billion in stages. This funding is intended to establish data centers filled with Nvidia technology.
The collaborations do not stop there. Nvidia has also committed to investing $5 billion in Intel, a company facing challenges in maintaining its manufacturing dominance. OpenAI has secured further financial backing from Oracle and SoftBank for its ambitious Stargate data center initiative in the United States. Additionally, funding from the United Arab Emirates is earmarked for a new data center in Abu Dhabi.
These financial ties underscore the interconnected nature of the AI ecosystem. OpenAI’s longstanding relationship with Microsoft has been restructured recently, further solidifying its role in the AI landscape. Meanwhile, OpenAI’s competitor, Anthropic, has attracted significant investments from both Google and Amazon, illustrating the competitive yet collaborative environment in which these companies operate.
Government Involvement and Financial Implications
The U.S. government has also entered the fray, becoming a stakeholder in the AI sector through initiatives such as the CHIPS Act, which aims to bolster domestic chip manufacturing. Under the terms of this act, the government has acquired a 10% ownership stake in Intel as part of a funding agreement designed to help the company recover its manufacturing capabilities.
Historically, periods of significant growth in industries, akin to the railroad expansions of the 19th century, have led to corruption and regulatory responses. The current environment, shaped by fast-paced dealings and a lack of oversight, raises concerns among industry veterans. The complexities of financing in the AI space, characterized by circular investments where one company funds another’s purchases, mirror the opacity observed during the dot-com bubble and the 2008 financial crisis.
As AI firms become increasingly intertwined, the risk of widespread fallout from individual setbacks escalates. OpenAI, which is currently a driving force in the AI industry, is closely tied to the broader U.S. economy. Should it falter, the repercussions may extend far beyond its immediate operations, affecting numerous stakeholders across the sector.
The evolving dynamics within the AI industry highlight the balance between collaboration and competition, as companies navigate an intricate web of partnerships and investments that could redefine the technological landscape.