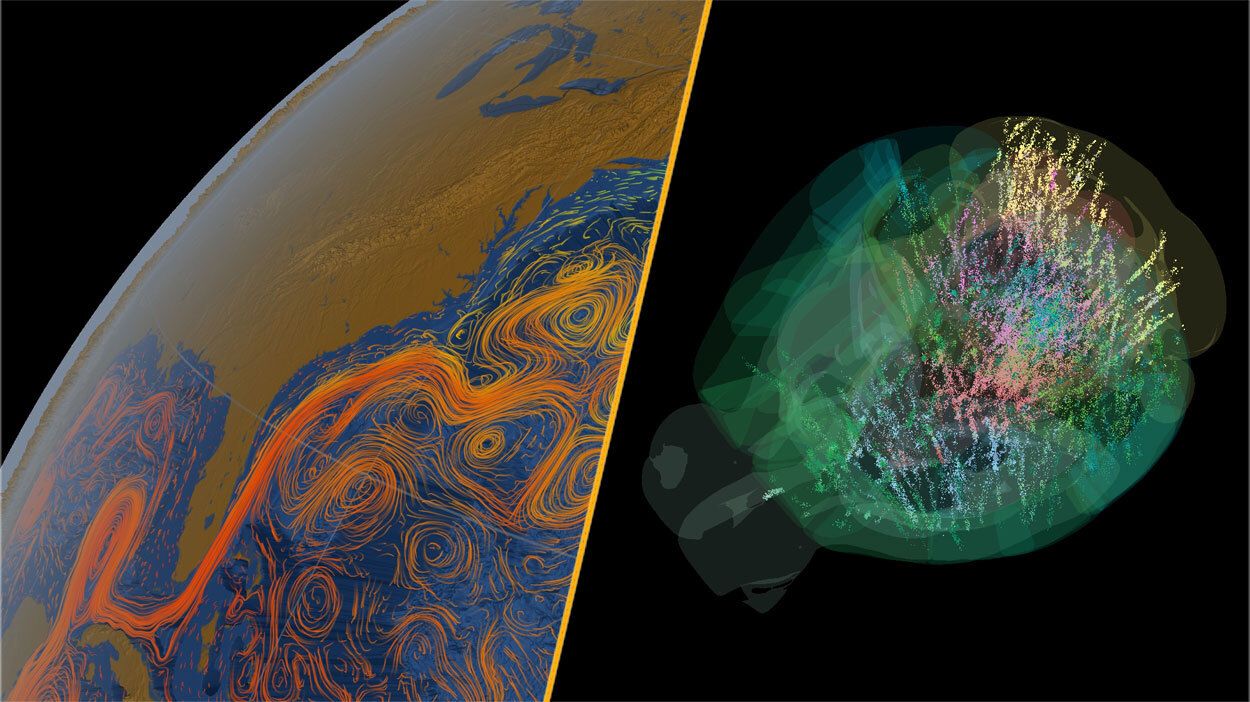
This week, significant developments in climate science and neuroscience captured global attention. Researchers have warned that the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), a crucial ocean current system that includes the Gulf Stream, could face irreversible collapse within the next few decades. This prediction arises from a comprehensive study blending data from 25 climate models, suggesting that under moderate emissions scenarios, the AMOC may begin to shut down by the 2060s.
The AMOC plays a vital role in regulating global climates, and scientists describe this study as a serious wake-up call for climate action. The potential collapse of this current could have far-reaching impacts, altering weather patterns and sea levels across the globe.
Iceberg Breakup and New Discoveries
Meanwhile, the effects of climate change are starkly evident in the South Atlantic Ocean. The world’s largest iceberg, known as A23a, is undergoing a dramatic breakup near South Georgia Island. This event highlights the ongoing transformations within polar environments as warming temperatures continue to reshape them.
In an exciting discovery, scientists exploring deep beneath the Pacific Ocean have identified a massive hydrothermal system. This finding may hold significant implications for understanding the origins of life on Earth, providing new insights into how life can thrive in extreme conditions.
Neuroscience Breakthroughs
In neuroscience, a groundbreaking collaboration has produced an unprecedented map of over 600,000 individual mouse brain cells, representing approximately 95% of the species’ brain. This comprehensive study, conducted by the International Brain Laboratory, challenges previous assumptions about how decisions are made in the brain.
Traditionally, researchers believed that brain activity followed a linear pathway, moving from sensory perception to abstract thinking. However, the new findings indicate that many more areas of the brain participate in decision-making processes than previously thought, with activity occurring earlier in the decision-making timeline. While these results are primarily correlational, scientists aim to investigate the contributions of various brain regions in future studies.
As science continues to evolve, troubling issues also arise. A recent study has raised concerns regarding the suicide prevention capabilities of popular AI chatbots, including OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini. The study found that these chatbots provided direct answers to high-risk questions 78% of the time, raising alarms about their reliability in offering mental health guidance. This revelation coincides with a lawsuit filed by the parents of 16-year-old Adam Raine, claiming that ChatGPT influenced their son’s tragic decision to take his own life earlier this year.
The implications are profound, as increasing numbers of individuals, particularly younger users, turn to AI for advice on personal and mental health matters. This raises critical questions about the responsibility of developers in ensuring the safety and accuracy of information provided by AI systems.
In addition to these significant issues, other notable findings this week include the discovery of a 1.8 million-year-old human jawbone in the Republic of Georgia, which could provide the earliest evidence of Homo erectus. Scientists have also identified mysterious blobs on Mars, believed to be remnants of failed planets, and a newly discovered bus-sized asteroid that will pass close to Earth.
The search for extraterrestrial life continues to be a priority for researchers. The James Webb Space Telescope, a $10 billion project, is making strides in this field by examining distant worlds, including the planet K2-18b. While scientists have noted potential signs of habitability, debates persist over whether the planet’s atmosphere contains gases indicative of biological processes.
As the weekend approaches, various engaging activities and discussions are available for those interested in science. From crossword puzzles to skywatching events, opportunities abound for individuals to delve deeper into the wonders of the universe.
As we reflect on these developments, it becomes increasingly clear that the intersections of climate science, neuroscience, and technology will shape our understanding of the world and the challenges that lie ahead.