A long-term multiwavelength study of the nearby blazar designated TXS 0518+211 has unveiled intricate emission patterns, according to research conducted by Indian astronomers. Utilizing data from NASA‘s Swift and Fermi space telescopes, the findings were made public on November 26, 2023, on the arXiv pre-print server, highlighting the complexity of this astronomical object.
Blazars are a specific type of active galactic nucleus, known for their exceptionally bright emissions across various wavelengths. The study of TXS 0518+211 is significant due to its proximity, located approximately 2.5 billion light-years away from Earth. This close distance allows astronomers to observe the blazar in greater detail compared to more distant counterparts.
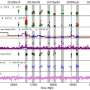
The research team monitored the blazar over an extended period, capturing data from both optical and high-energy gamma-ray observations. Results indicated that the emission patterns of TXS 0518+211 are far more complex than previously understood. These variations in brightness and frequency can offer insights into the physical processes occurring within the blazar.
Importance of the Findings
Understanding the emission patterns of blazars like TXS 0518+211 is crucial for astrophysics, as it provides clues about the mechanisms behind their energetic emissions. The data suggest that interactions between different particles and magnetic fields may play a significant role in the blazar’s behavior. This finding could enhance the broader understanding of similar astronomical phenomena.
The collaboration between NASA‘s telescopes has proven instrumental in this research. The Swift telescope’s capability to rapidly observe transient astronomical events, combined with the Fermi telescope’s expertise in capturing gamma rays, formed a robust framework for studying this blazar’s emissions.
Future Implications
The implications of this research extend beyond the study of TXS 0518+211. As astronomers continue to analyze and interpret the data, further insights may arise regarding the evolution of blazars and their impact on the universe. This study not only adds to the existing body of knowledge but also raises new questions about the nature of these cosmic entities.
As observational technology continues to advance, the potential for new discoveries in the field of astrophysics remains vast. The work of the Indian astronomers represents a significant step forward in understanding the complexities of blazars and their role in the cosmic landscape.