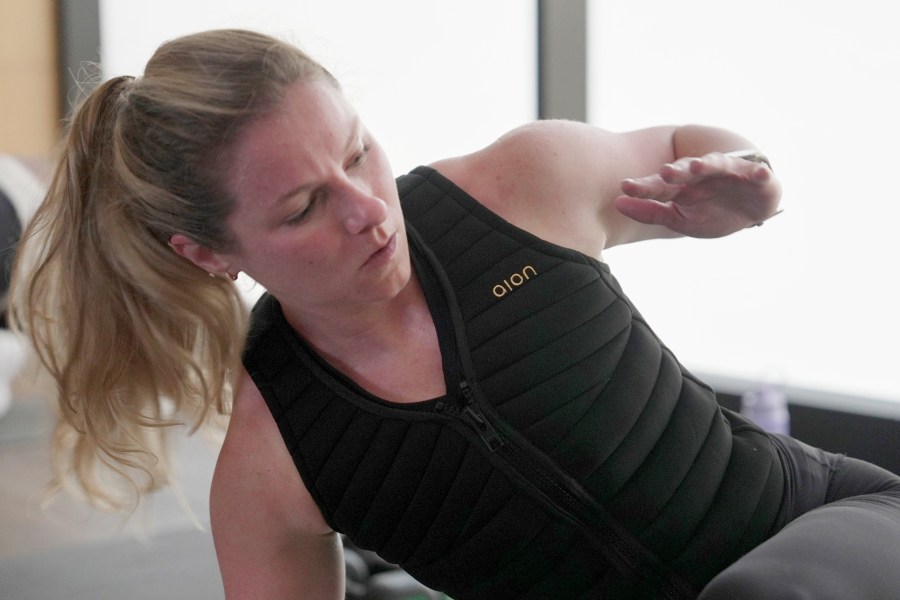
Fitness enthusiasts are increasingly turning to weighted vests as a way to enhance their workouts, adding an extra layer of resistance to traditional exercises. In classes created by Jessie Syfko, senior vice president for Life Time gyms, participants wear these vests to challenge themselves further. Syfko emphasizes that individuals begin to appreciate the benefits of exerting “just a little bit harder and a little bit smarter” without fundamentally changing their routines.
The popularity of weighted vests is growing, particularly among fitness influencers who promote them as tools for improving bone health, boosting athletic performance, and accelerating weight loss. These vests work by incorporating removable weights into pockets designed for this purpose, making them straightforward in concept. However, experts caution that robust research on their effectiveness is still lacking, raising questions about how much of the current enthusiasm is warranted.
Potential Benefits of Weighted Vests
The science behind using weighted vests suggests that they can assist with fitness goals like weight loss, muscle growth, and bone density maintenance. By adding weight to the torso, users experience increased resistance during their daily activities without altering their existing patterns.
According to Jeff Monaco, a certified strength coach at the University of Texas at Austin, while the calorie burn may not be drastically higher, the added resistance can lead to improved sports performance over time. He notes, “There are a lot of studies looking at (the weighted vest) from a speed perspective in different athletics, like soccer, with changing direction, agility, and speed.”
Monaco recommends that individuals incorporate about 10% of their body weight into the vest for optimal benefits. For someone weighing 150 pounds, this means adding approximately 15 pounds to their vest. Despite the potential benefits, research outside the realm of athletics is less definitive.
A study conducted by the Wake Forest University School of Medicine in 2020 examined adults aged 60 to 85. The findings indicated that those who wore weighted vests during periods of high activity experienced similar weight loss and bone density loss as those who did not wear them. This suggests that while weighted vests may offer some advantages, they should not be solely relied upon for substantial health improvements.
Guidelines for Safe Use
Experts recommend caution when using weighted vests, particularly for those new to resistance training. It is advisable to start with a weight that is between 5% and 10% of an individual’s body weight. Overloading the vest can lead to excessive strain on joints, back, and hips, potentially resulting in poor posture or injuries such as stress fractures.
Certain individuals should consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating weighted vests into their exercise routines. Dr. Elizabeth Gardner, a team physician for athletes at Yale University, advises that pregnant individuals or those with heart, breathing, or musculoskeletal conditions should be especially mindful. “You’ll have to use the muscles in your abdomen to use a weighted vest effectively,” she explains, noting that this can be challenging for those managing back pain.
Monaco also underscores the importance of receiving proper guidance when starting to use a vest. He advises working with a knowledgeable trainer to ensure correct movement and form, as well as to confirm that one possesses adequate upper body strength to handle the additional weight during exercises.
In conclusion, when utilized properly, a weighted vest can serve as a valuable tool for enhancing workout routines. As the fitness community continues to explore its benefits, careful implementation and consideration of individual health needs remain essential.
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content.