Researchers from Tianjin University have introduced a new approach to enhancing the resilience of biofuel supply chains. Their study, titled “Optimization Design Method for Biofuel Resilient Supply Chain Considering Node Disruption Impacts in a Two-Stage Stochastic Programming Framework,” was published in Frontiers of Chemical Science & Engineering, Volume 19, Issue 6. The research addresses the growing complexities and uncertainties faced by businesses in the biofuel sector as economic globalization accelerates.
As supply chain systems expand, they encounter an increased risk of disruptions. This makes it critical for companies to design biofuel supply chains that can withstand such challenges while ensuring security and competitiveness. Traditional methods for designing these supply chains often fall short in effectively quantifying and evaluating the risks associated with disruptions.
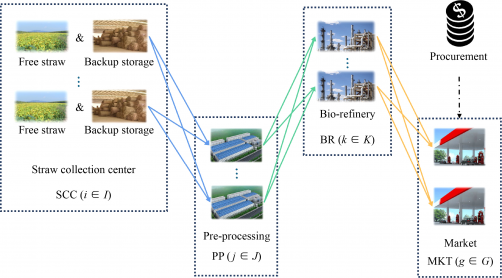
To tackle this issue, the study proposes an improved Node Disruption Impact Index with adjustable parameters. This index is based on the cost changes triggered by disruptions at various nodes within the supply chain. By enabling the identification of nodes with different risk levels, this tool provides a framework for evaluating the impact of disruptions. The adjustable parameters allow businesses to tailor the index to their specific needs, thereby balancing economic benefits with supply chain resilience.
Innovative Modeling for Supply Chain Optimization
The researchers also developed a two-stage stochastic programming supply chain optimization model that incorporates mechanisms to address potential high disruption risks. This model was applied to a case study involving a biofuel supply chain in Guangdong Province. The results revealed that, in scenarios where high-risk nodes were disrupted, the proposed model significantly outperformed traditional models in terms of both cost efficiency and market delivery rates.
The findings underscore the effectiveness of this innovative approach in optimizing the design of resilient supply chains. By equipping businesses with the tools to better manage risks, this research significantly contributes to the field of supply chain management, particularly within the biofuel sector.
For further insights and detailed findings, the full paper can be accessed at: https://journal.hep.com.cn/fcse/EN/10.1007/s11705-025-2548-z.