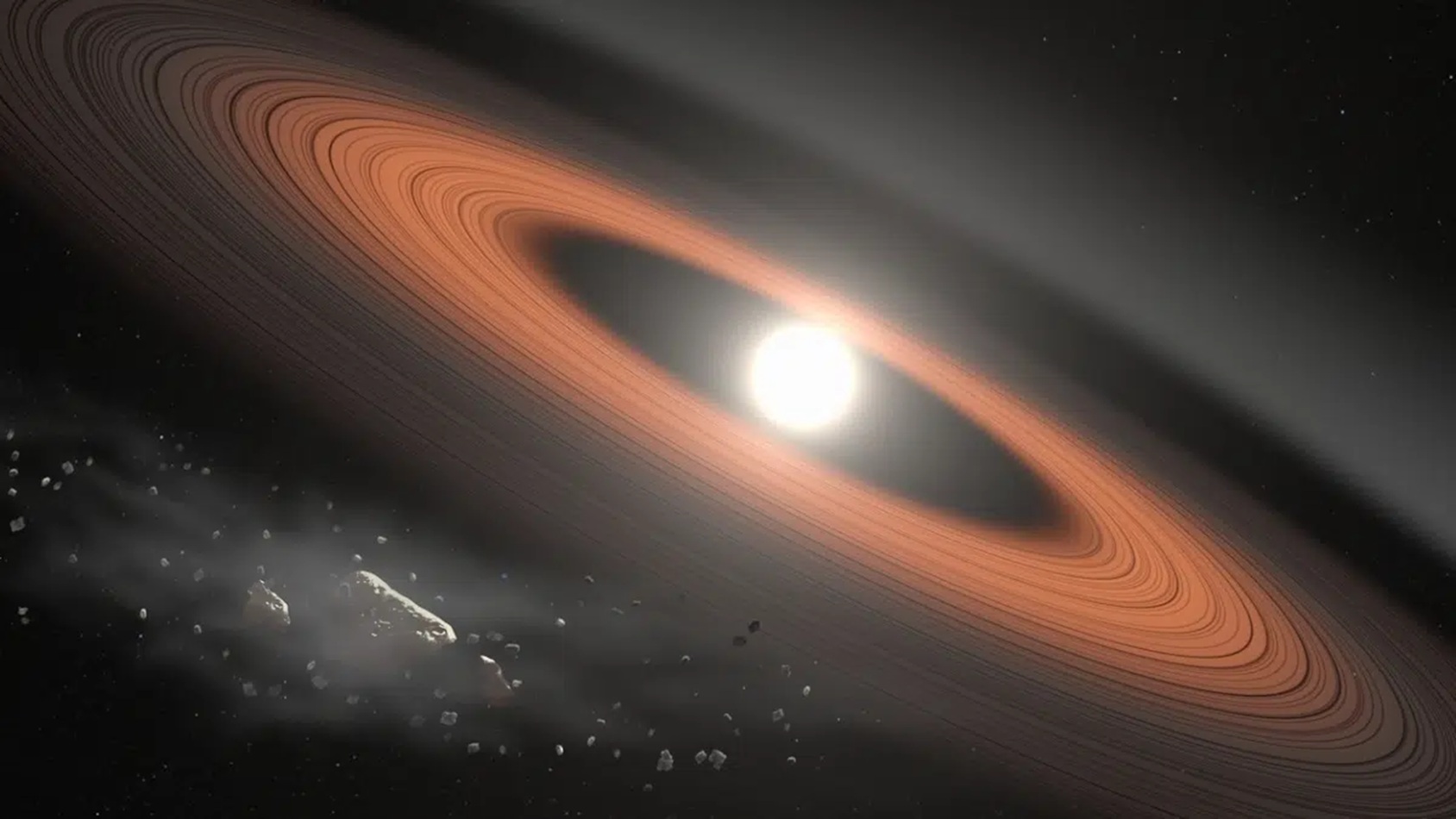
Astronomers have made a groundbreaking observation of a dying star consuming a shattered planet. This remarkable event offers insight into the ultimate fate of Earth when the sun reaches the end of its life cycle. The findings, published by IOPscience, reveal critical details about the dynamics of planetary destruction and the life cycle of stars.
The phenomenon was observed in a distant planetary system located in the Milky Way. Researchers used advanced telescopic technology to capture the moment when the dying star, known as a red giant, began to engulf the remnants of a planet that had been torn apart. This event serves as a stark reminder of the inevitable transformations that await our own solar system.
Significance of the Discovery
The implications of this observation extend beyond mere curiosity. The study highlights the processes that lead to the destruction of planetary bodies, offering a glimpse into what may occur when the sun exhausts its nuclear fuel. Astronomers suggest that, in approximately 5 billion years, our sun will enter a similar phase, expanding into a red giant and potentially consuming the inner planets, including Earth.
This research sheds light on the lifecycle of stars and the fate of planetary systems. By understanding these processes, scientists can better predict the long-term outcomes for celestial bodies. The event’s documentation not only enriches our knowledge of astrophysics but also raises questions about the future viability of life in the universe.
Future Research Directions
The observations made during this event will likely prompt further studies into the effects of stellar evolution on surrounding planets. Researchers plan to analyze the debris from the shattered planet to better understand its composition and the conditions that led to its destruction. Such investigations will provide valuable context on how similar events could unfold in our own solar system.
Moreover, these findings could inform the search for extraterrestrial life. If planets can be destroyed by their stars, the search for habitable environments must consider the lifecycle stages of stars more carefully. This research emphasizes the importance of studying distant systems to gain insights into our own celestial neighborhood.
In conclusion, the observation of a dying star consuming a shattered planet not only enhances our understanding of stellar evolution but also serves as a poignant reminder of the eventual fate awaiting our own planet. As astronomers continue to unravel the mysteries of the universe, discoveries like this deepen our appreciation for the complex and dynamic nature of cosmic life cycles.