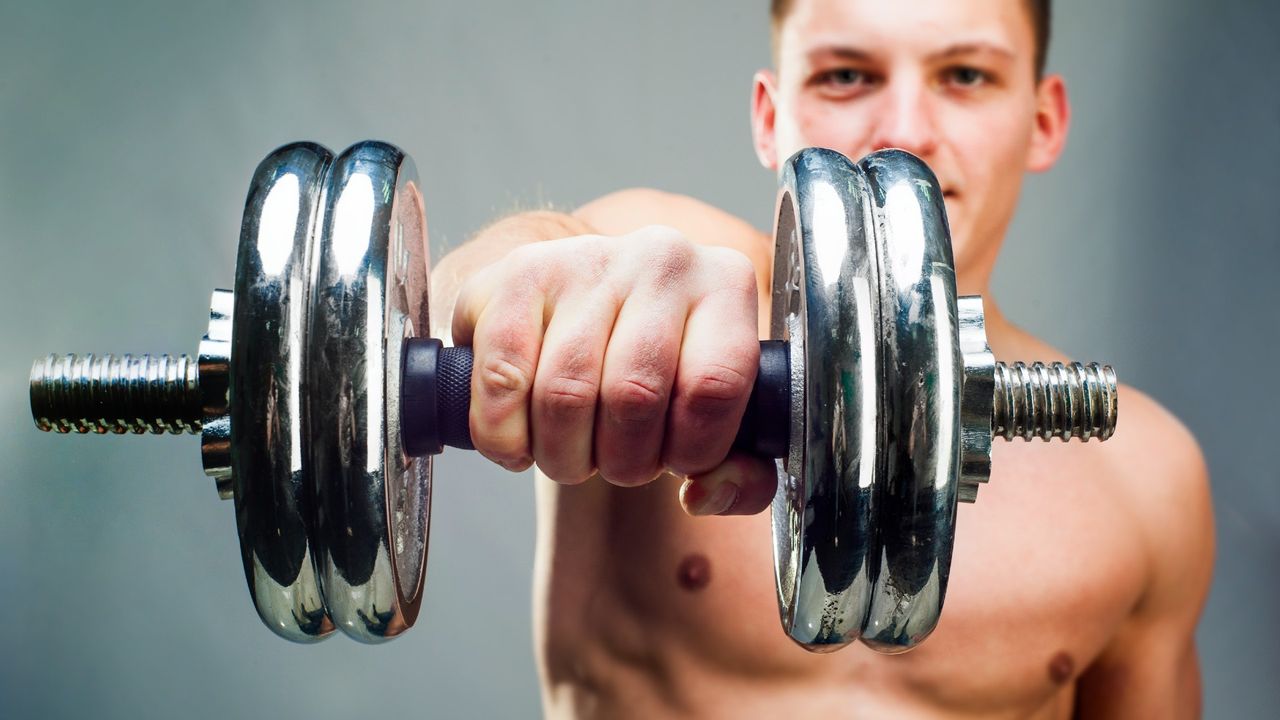
A personal trainer recently explored the use of artificial intelligence to develop a strength training program specifically focused on muscle growth. The trainer utilized ChatGPT to create a four-week German Volume Training (GVT) program, ultimately expressing surprise at the program’s effectiveness. This initiative reflects a growing trend where fitness enthusiasts turn to AI for accessible and cost-effective workout solutions.
In this experiment, the trainer aimed to develop a full-body muscle-building routine using only a barbell and a set of dumbbells. GVT involves performing 10 sets of 10 repetitions for two compound exercises during each session, followed by optional accessory exercises. The approach is designed to stimulate significant muscle mass growth without requiring excessive time in the gym.
The trainer began by requesting ChatGPT to construct a four-week program tailored to their experience level and fitness goals. They specified their maximum lifting loads: 35 kg for front squats and 25 kg for bench presses, while also requiring that the program adhere to GVT principles of high volume and progressive overload.
ChatGPT responded by suggesting a detailed program that maintained the GVT structure while allowing for gradual increases in weight. The AI proposed a regimen that included exercises such as barbell front squats, dumbbell overhead presses, and barbell rows. The program also recommended a controlled lifting tempo, emphasizing a slow eccentric phase for increased effectiveness.
Despite the promising results, the trainer noted certain limitations inherent in using AI for personal training. While ChatGPT provided a well-structured program, the trainer emphasized that no AI could fully replicate the adaptability and personal touch of a human trainer. Human trainers can adjust workout plans based on real-time feedback, ensuring that clients maintain proper form and stay motivated during challenging sessions.
The AI-generated program included progressive weight increments of 2.5 kg each week, provided the trainer could complete all repetitions with proper form. This aspect aligns well with GVT’s core principle of progressive overload, which is essential for muscle development.
One notable feature of the program was its focus on compound exercises, which target multiple muscle groups simultaneously, thereby maximizing workout efficiency. The trainer appreciated that ChatGPT included accessory exercises aimed at complementing the primary lifts while preventing overtraining.
Throughout the four weeks, the trainer tracked their progress and found that the structured approach allowed for consistent improvements in strength and endurance. However, they also recognized the responsibility placed on users to assess their form and determine when to increase weights, underscoring the necessity of self-awareness in any training regimen.
In conclusion, while the experiment with ChatGPT’s GVT program yielded positive outcomes, the trainer remains cautious about the reliance on AI in fitness training. They believe that for individuals seeking tailored and responsive coaching, the presence of a knowledgeable human trainer is invaluable. As technology continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how AI tools like ChatGPT integrate into personal training and whether they will complement or compete with traditional training methods.