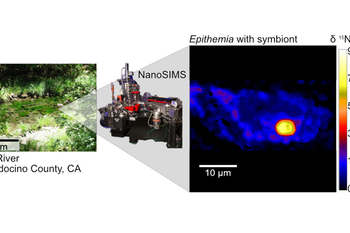
A unique river ecosystem has demonstrated a remarkable ability to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form of fertilizer, providing new insights into sustainable nitrogen production. This discovery could significantly impact agriculture, where nitrogen fertilizers play a crucial role in enhancing crop yields.
Researchers from various institutions have focused on this ecosystem, located in a river basin that supports diverse plant and animal life. Their findings indicate that natural processes within this environment efficiently convert nitrogen from the air, making it available for use in agriculture without the high energy costs associated with traditional fertilizer production.
Understanding how this ecosystem operates could lead to innovative approaches to nitrogen fertilizer manufacturing. Currently, approximately 1.5% of the world’s energy is consumed in the process of producing nitrogen fertilizers, primarily through the Haber-Bosch method. This method, while effective, releases substantial carbon emissions, raising concerns about its environmental impact.
Research Findings and Implications
The research team, which includes scientists from leading universities and environmental organizations, published their findings in Nature Communications on March 10, 2024. They outline how certain microorganisms within the river ecosystem facilitate the conversion of nitrogen gas into ammonia, a critical component of fertilizers. This biological process, known as nitrogen fixation, occurs naturally and could be harnessed to develop more sustainable agricultural practices.
The implications of this research are far-reaching. With the global population expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, the demand for food will increase significantly. Sustainable nitrogen production methods could help meet this demand while minimizing environmental degradation. The research emphasizes the need for a shift away from energy-intensive fertilizer production methods towards more eco-friendly alternatives.
Investing in the study of such ecosystems is essential for developing innovative agricultural solutions. The researchers advocate for increased funding and support for projects exploring natural nitrogen fixation processes, which could lead to breakthroughs in sustainable farming practices.
Future Directions in Agriculture
The findings from this river ecosystem not only provide a blueprint for sustainable nitrogen production but also highlight the importance of preserving natural habitats. As more ecosystems are threatened by human activity, understanding their mechanisms could offer vital solutions to global agricultural challenges.
Efforts to replicate these natural processes in agricultural settings are already underway. By employing similar microorganisms or mimicking the environmental conditions found in the river ecosystem, agricultural scientists hope to create fertilizers that require less energy and have a lower carbon footprint.
In conclusion, the potential of this river ecosystem to convert air into fertilizer presents an exciting opportunity for sustainable agriculture. As researchers continue to explore these natural processes, the agricultural sector may soon benefit from innovative solutions that not only enhance food production but also protect the environment.