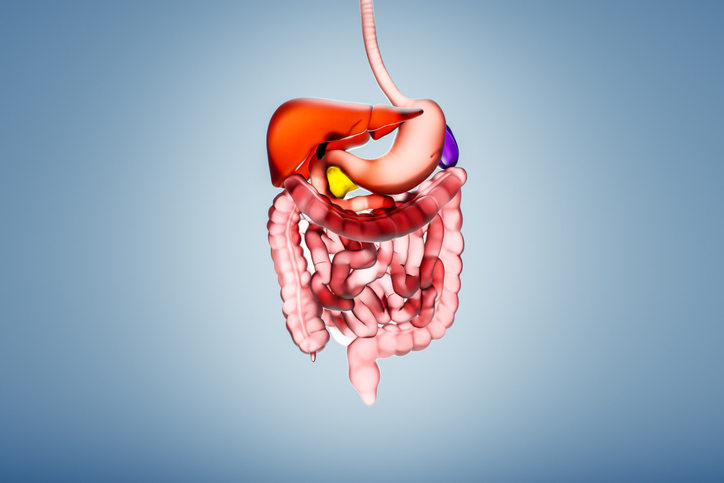
The management of gastrointestinal (GI) conditions is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by increasing public interest in gut health and advancements in medical research. Over the past decade, conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) have shifted from being perceived primarily as psychological issues to recognized physical health concerns. This evolution stems from a combination of consumer awareness and breakthroughs in understanding the gut microbiome, significantly impacting treatment strategies.
Integrating Nutrition into GI Care
A notable shift in gastroenterology is the enhanced focus on nutrition as a vital component of patient care. The recognition of dietary strategies, particularly the Low FODMAP diet and Low Fermentation Eating, has gained traction as effective methods for managing symptoms of IBS and SIBO. The concept of “food as medicine” is increasingly embraced by both healthcare professionals and patients.
As part of this integrated approach, gastroenterologists are now collaborating with gastrointestinal registered dietitians (GRDs). These specialists help patients navigate their unique dietary needs, creating tailored nutrition plans that complement traditional medical treatments. This combination can lead to more effective long-term management of chronic GI conditions.
For instance, while antibiotics have historically been the first line of treatment for SIBO, their success rate is only around 44%. In contrast, a palatable elemental diet has shown an impressive 83% eradication rate for SIBO, illustrating the potential of nutrition-based interventions in enhancing patient outcomes.
Technological Advancements in Diagnosis
Technology is revolutionizing GI patient care, streamlining diagnosis and treatment processes. In 2020, the introduction of the first three-gas breath test marked a significant milestone in non-invasive diagnostics. This test evaluates exhaled hydrogen, methane, and hydrogen sulfide, enabling the identification of conditions like SIBO, intestinal methanogenic overgrowth (IMO), and intestinal sulfide overproduction (ISO) more accurately and rapidly.
With home-testing options available, patients can now access important diagnostic tools without the need for invasive procedures, which often involve long wait times and significant costs. This accessibility allows for earlier intervention, reducing the burden of debilitating symptoms while also minimizing financial strain on patients.
Mobile applications designed to support integrated care plans are also emerging in the GI field. These tools provide virtual assistance for lifestyle management, helping patients address factors such as stress and dietary habits that can exacerbate GI conditions. Some apps have received FDA approval, offering patients additional resources for managing their health.
Consumer trends are increasingly influencing GI treatments, with patients often drawn to various health products promoted on social media. While prebiotics and probiotics have gained popularity, gastroenterologists frequently find themselves addressing misconceptions surrounding these products. Many patients are unaware that not all probiotics are beneficial, especially if their gut issues stem from an imbalance of bacteria.
As the wellness landscape continues to evolve, healthcare providers must remain vigilant in educating patients about the implications of these trends, ensuring that they receive evidence-based recommendations rather than relying solely on influencer endorsements.
The evolution in the management of GI disorders is not just a matter of medical advancements; it represents a significant shift in patient experiences. By embracing nutritional strategies and leveraging technological innovations, healthcare providers are better equipped to deliver comprehensive care.
While research into the gut microbiome continues to deepen our understanding, it is essential for policies and reimbursement structures to adapt in order to support these advancements in GI care. Collaboration between medical professionals and nutrition experts is key to empowering patients and fostering improved health outcomes.
The ongoing journey towards better management of GI conditions is indicative of a broader movement in healthcare, aiming for an integrated, patient-centered approach that prioritizes holistic well-being. As new diagnostic methods and treatment options emerge, patients can look forward to more effective and personalized care in the realm of gastrointestinal health.