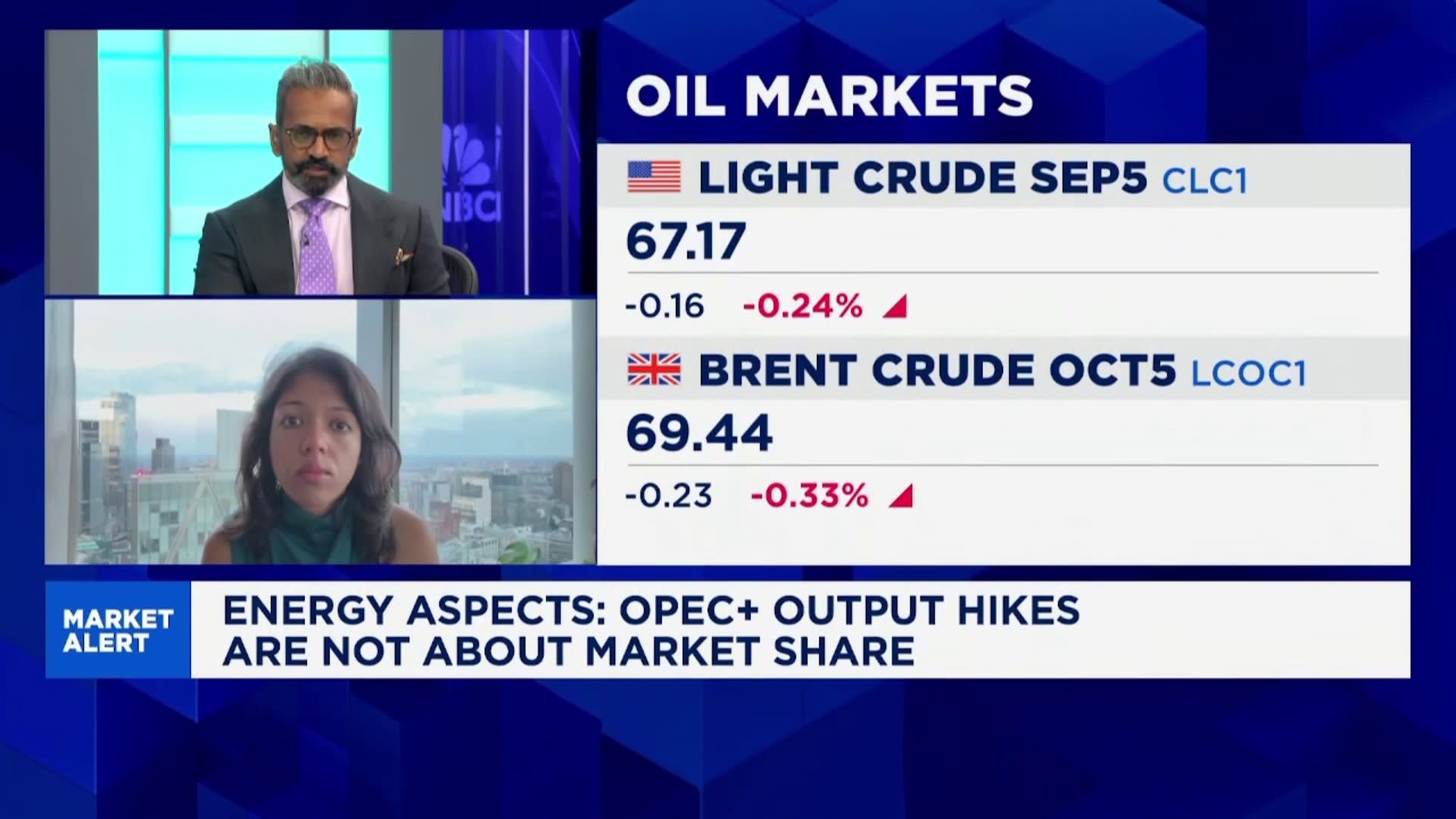
New insights from Energy Aspects reveal that the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is prioritizing market stability over market share in its current energy policy. This shift indicates a strategic move away from competitive pricing aimed at maintaining or increasing production levels, instead emphasizing price stability to support global economic recovery.
According to the report released on September 25, 2023, OPEC recognizes that pursuing market share could lead to volatility within the oil market. Instead, the organization is focusing on a balanced approach to oil production, which aims to prevent large fluctuations in prices that can disrupt economic stability worldwide.
OPEC’s Strategic Reorientation
The energy landscape has changed significantly in recent years, partly due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and ongoing geopolitical tensions. OPEC’s decisions are now more reflective of a desire to foster a stable environment for both producers and consumers. The report from Energy Aspects underscores that OPEC members are increasingly aware that excessive production can lead to oversupply, which in turn depresses prices and harms the overall market.
As a result, the organization is likely to continue implementing production cuts when necessary to stabilize prices. For instance, the recent agreement among OPEC+ members to extend production cuts into 2024 aims to support oil prices, which have shown signs of recovery but remain sensitive to changes in global demand.
In Vienna, where OPEC’s headquarters is located, discussions among member nations have centered on how to balance production levels with the ongoing recovery of the global economy. The focus on stability aligns with the broader goals of many member countries that rely heavily on oil revenues to fund government budgets and public services.
Implications for the Global Oil Market
This strategic pivot could have significant implications for the global oil market. By prioritizing price stability, OPEC may influence global energy prices, impacting everything from consumer gasoline costs to the economic health of oil-dependent nations. Analysts suggest that this approach may foster a more predictable pricing environment, which could enhance investment in energy infrastructure and alternative energy sources.
In a volatile market, prices can swing dramatically, affecting not only the oil sector but also various industries reliant on stable energy costs. OPEC’s new direction could help mitigate these fluctuations, providing a firmer foundation for economic growth across multiple sectors.
The findings from Energy Aspects indicate that OPEC’s decisions will continue to play a critical role in shaping the future of the oil market. As the global economy evolves, the organization’s focus on stability rather than market share could become a defining characteristic of its energy policy, influencing both short-term actions and long-term strategies.
In conclusion, as OPEC navigates the complexities of the modern energy landscape, its commitment to stability over competition could set a new precedent for how oil-producing nations approach market dynamics in the years to come.