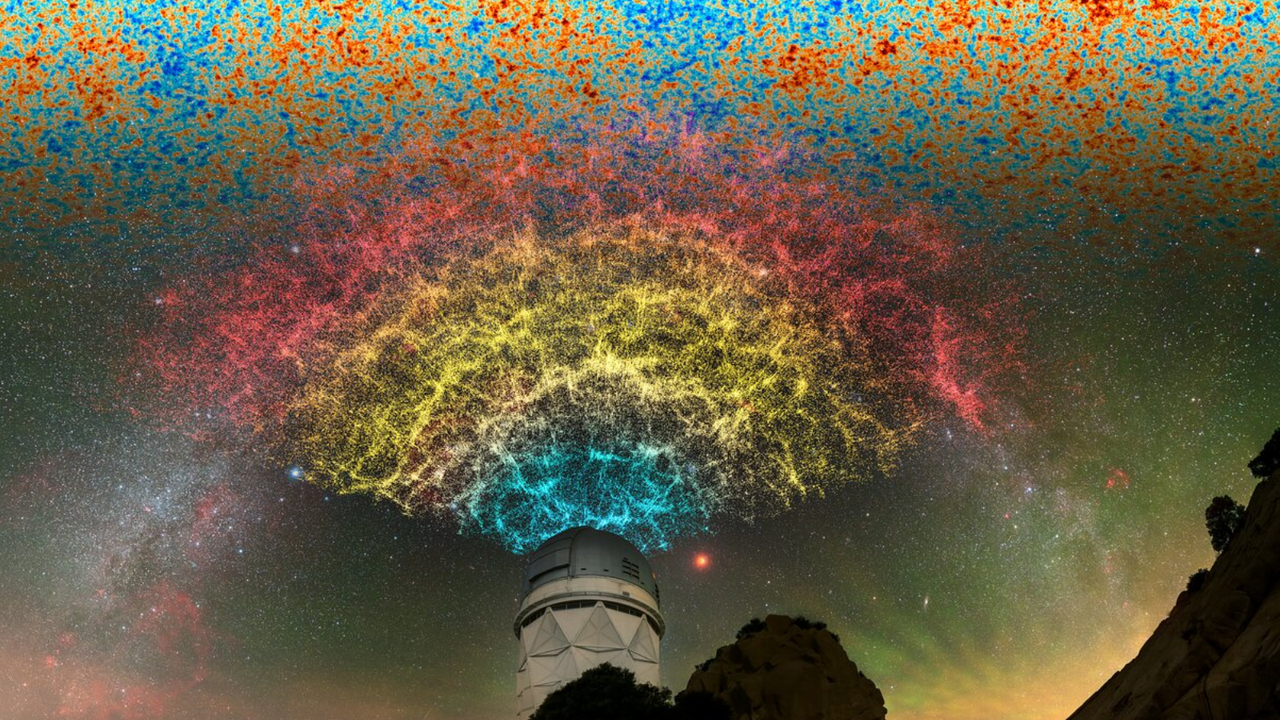
BREAKING: Astronomers have just revealed that the universe may meet its end in a shocking 33 billion years, significantly sooner than previously thought. New evidence suggests that dark energy, the mysterious force driving the universe’s accelerated expansion, may not be as constant as once believed.
This urgent update stems from recent findings by the Dark Energy Survey (DES) and the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI). These extensive galaxy surveys indicate that dark energy could be evolving over time, challenging the long-held cosmological constant model. If validated, this discovery would profoundly alter our understanding of cosmic dynamics.
The implications are staggering. The research, which was presented in a yet-to-be-peer-reviewed paper in June, proposes a groundbreaking model of dark energy consisting of two components: an axion and a modified cosmological constant. Axions, hypothetical ultralight particles, could fill the universe, driving the current phase of accelerated expansion. However, as time progresses, their influence will wane, allowing a negative cosmological constant to take precedence.
This transformation would initiate a deceleration of the universe’s expansion, leading to a catastrophic “Big Crunch.” The theorists predict this collapse phase could begin in just 10 billion years, meaning we are witnessing a universe that, while not at midlife, is advancing toward its maximum size.
The potential for a universe that ultimately collapses back into a singularity mirrors the events of the Big Bang. Galaxies would merge, the universe would grow hotter and denser, culminating in a dramatic end.
While these findings are groundbreaking, scientists caution that they are still in the preliminary stages. The results from DES and DESI require further validation, and the proposed model remains theoretical. However, if confirmed, it could reshape our cosmic perspective and ignite discussions about the universe’s fate.
As we stand on the brink of these revelations, the urgency to further explore dark energy has never been more pronounced. This research not only expands our understanding of the universe but also evokes emotional contemplation about humanity’s place in the cosmos.
In the coming months, experts will continue to analyze DES and DESI’s findings, and the scientific community will be eagerly watching for peer-reviewed publications that could either confirm or challenge this radical new model. The universe may have far more surprises in store for us than we ever anticipated.
Stay tuned for more updates as scientists race to unravel the mysteries of dark energy and its implications for our universe’s fate.