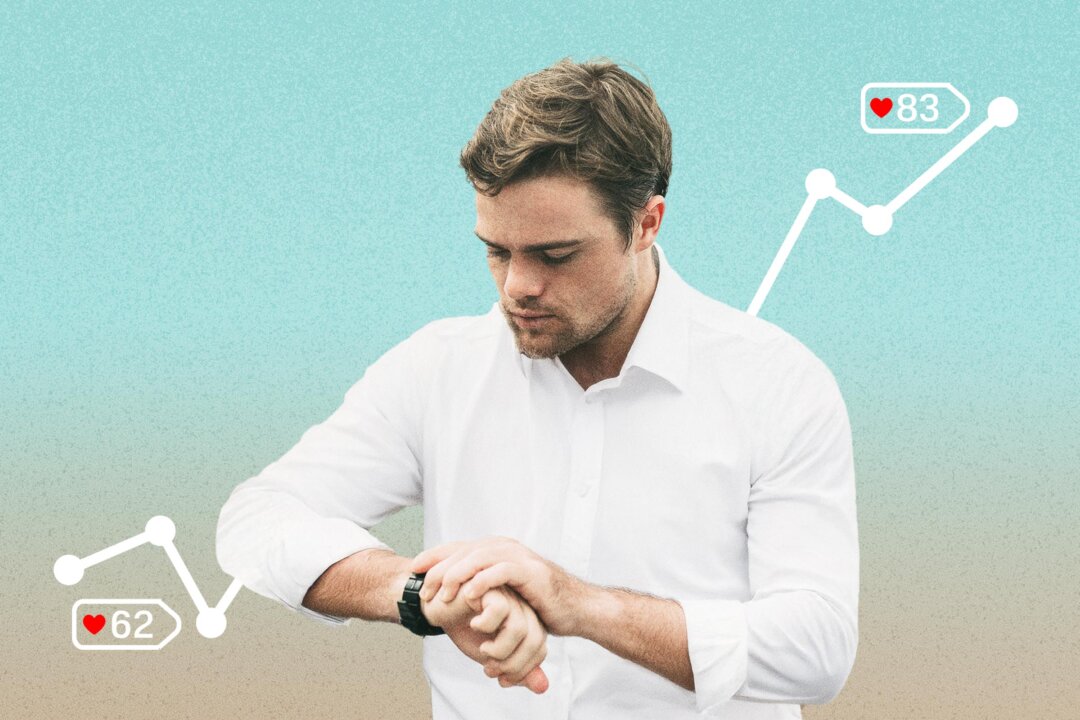
A recent experience for Dr. Michael Snyder, a geneticist at Stanford University, highlights the importance of monitoring heart health through wearable technology. During a flight to Norway, Snyder noticed unusual readings from his smartwatch—his heart rate and oxygen levels remained elevated long after takeoff. This anomaly prompted him to seek medical attention, leading to a diagnosis of Lyme disease days later.
Snyder’s situation underscores how wearable devices can serve as critical tools for early health detection. He described the moment, stating, “Resting heart rate is definitely an indicator of all kinds of stress—physical and mental,” in an interview with The Epoch Times.
Smart Technology as a Health Ally
Wearable technology, such as smartwatches, has increasingly become integral to personal health management. These devices monitor vital signs and can alert users to potential health issues before they manifest as more severe symptoms. In Snyder’s case, his smartwatch detected changes that signaled something was wrong, even when he felt fine.
Lyme disease, caused by the bite of an infected tick, often presents with symptoms such as fever, headache, and fatigue. However, in many cases, these symptoms can be subtle or mimic other illnesses, making early detection challenging. Snyder’s experience illustrates how technology can bridge this gap, potentially leading to quicker diagnoses and treatment.
The Importance of Monitoring Resting Heart Rate
Snyder’s elevated heart rate during the flight serves as a reminder of the significance of monitoring resting heart rates. Research indicates that fluctuations in heart rate can indicate stressors affecting both physical and mental health.
In light of Snyder’s experience, health experts emphasize the need for individuals to pay attention to their heart rate data, particularly when it deviates from their baseline. By doing so, people may be able to catch health issues early, allowing for timely intervention and improved outcomes.
As more individuals adopt health-monitoring technologies, the potential for proactive health management continues to grow. Snyder’s case not only highlights the immediate benefits of these technologies but also sets the stage for a broader discussion about the future of personal health monitoring.
The intersection of technology and health presents exciting opportunities for early detection and ongoing wellness. As this trend evolves, it may change how individuals approach their health and well-being, encouraging a more proactive stance toward personal health management.