Innovative advancements in electronic components are reshaping the traditional designs of potentiometers. T. K. Hareedran has introduced a new approach that utilizes magnetic sensing rather than the conventional contact-based mechanisms. This shift aims to improve accuracy and durability in applications that require precise voltage control.
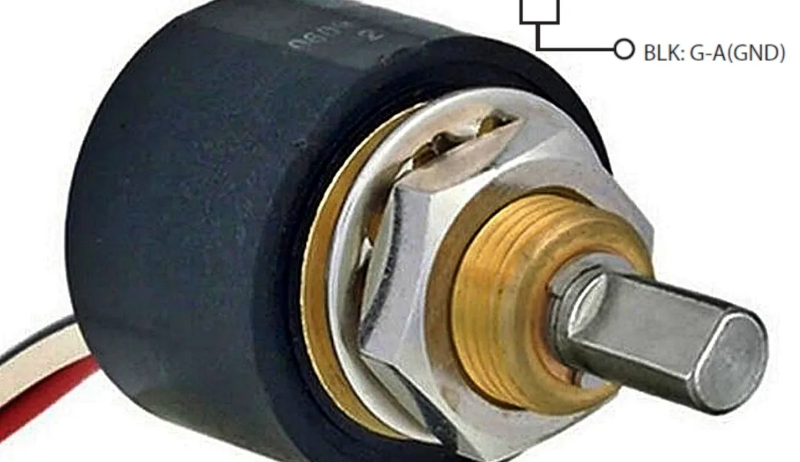
Traditional potentiometers consist of a resistive material with a movable contact that alters resistance as the shaft is rotated. While this design has been widely used, it comes with inherent limitations. The contacts can wear out over time, leading to inaccuracies. Additionally, temperature fluctuations and contamination can affect their performance. Hareedran’s magnetic potentiometers address these issues by employing a different mechanism altogether.
Understanding Magnetic Potentiometers
The devices discussed by Hareedran, such as the SK22B, operate on principles similar to rotary encoders. Instead of providing a resistive output, they generate a voltage output ranging from 10% to 90% of a 5 V input. This design simplifies the connection and enhances the linearity of the output compared to traditional models.
The key advantage of magnetic potentiometers lies in their longevity and reliability. Without physical contacts that wear out, these devices can operate effectively over extended periods. Hareedran notes that while these units do not function as traditional potentiometers, they serve a crucial role in applications requiring consistent voltage readings.
Building Non-Contact Sensors
Hareedran further explores the creation of a non-contact sensor that utilizes photosensors and a gray-coded wheel. This innovative design allows for more precise control without the drawbacks associated with contact-based systems. However, the positioning of the sensors is critical to ensure optimal functionality.
While the potential for non-contact resistive potentiometers exists, creating one that matches the efficiency of traditional designs remains challenging. Suggestions have been made for incorporating an FET output stage, although such a solution may not be as widely applicable as conventional carbon-based designs.
As the field of electronics evolves, the exploration of alternative approaches to traditional components continues. Hareedran invites feedback and ideas from the community, encouraging innovators to share their insights or build upon his concepts. This collaborative spirit is vital for driving progress in technology and enhancing the tools available to engineers and designers.
In summary, the emergence of magnetic potentiometers presents a promising alternative to traditional designs. With their advantages in accuracy and longevity, these devices could become increasingly prevalent in various applications, paving the way for more robust electronic systems.