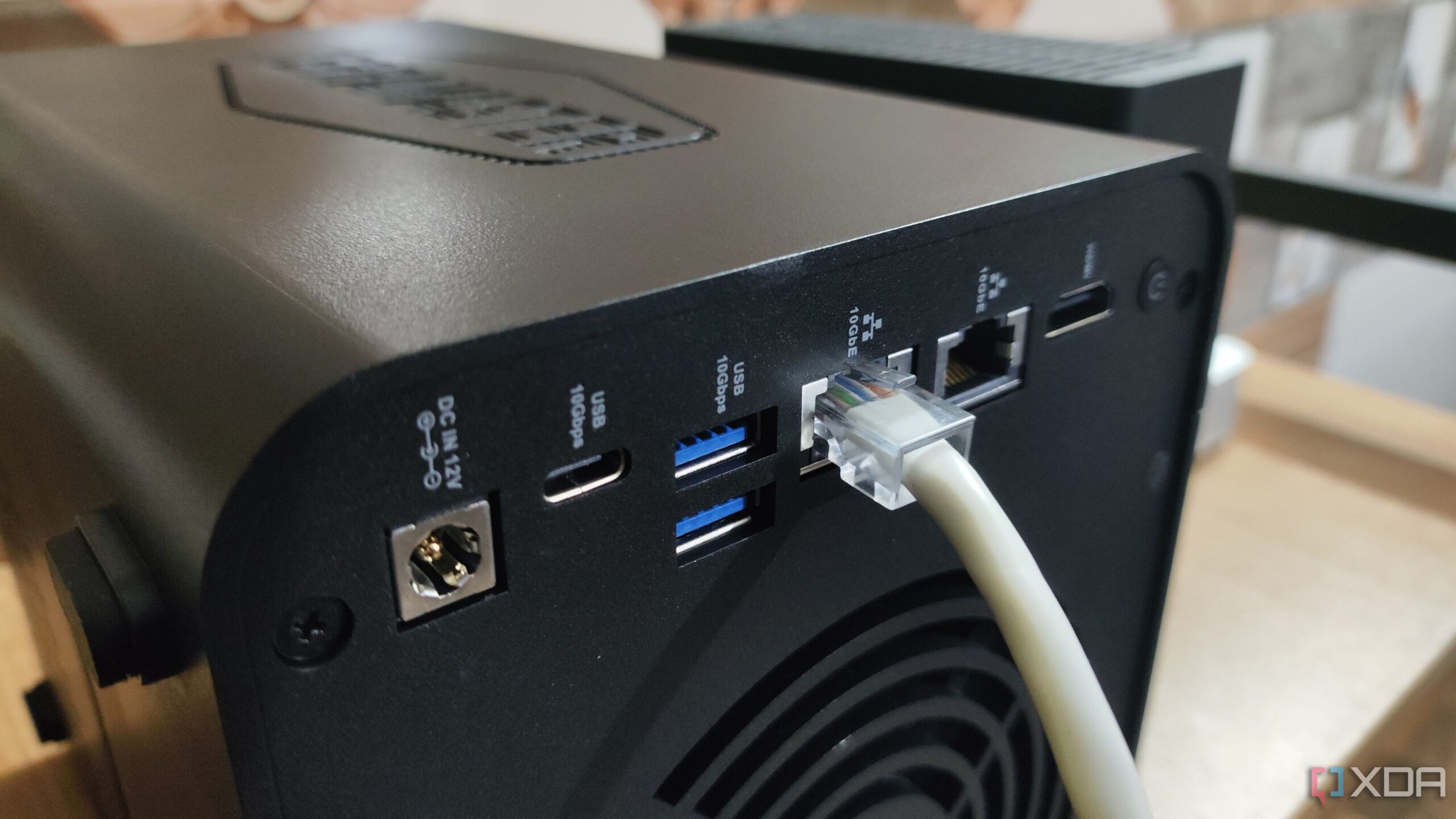
UPDATE: Home users are experiencing a significant boost in NAS performance thanks to the implementation of link aggregation. This technology, which allows for the simultaneous use of multiple network cables, is revolutionizing data transfer for families sharing devices.
In a recent hands-on trial, a user discovered that link aggregation enhances overall network performance, particularly when multiple devices access the NAS at the same time. While the initial expectation was for a simple doubling of transfer speeds—especially for large files like a 50GB video—the reality proved to be more nuanced. Individual transfers still maxed out at 1Gbps due to lane limitations; however, the real game changer came in the form of improved simultaneous usage.
As the user transferred their large video file, another device initiated a backup process. Typically, such simultaneous tasks would choke the network, resulting in slowdowns for everyone connected. But with link aggregation in place, the NAS managed these tasks efficiently, allowing for full-speed transfers and timely backups without conflict. This has proven to be a crucial upgrade in a shared household environment.
The benefits of link aggregation extend beyond just speed. With an additional connection in place, users gain enhanced redundancy. Should one cable or port fail, the system remains operational, ensuring uninterrupted access to files and media—even during peak usage times, like Tuesday mornings when backups are common.
For families who rely on shared media storage and streaming services like Jellyfin and Plex, this technology can dramatically enhance the user experience. Viewers no longer experience frustrating interruptions during high-demand moments, such as watching a popular series in 4K, thanks to the smoother data flow.
However, potential users must be aware that setting up link aggregation is not without its challenges. It requires a compatible hardware setup that supports the LACP standard at every point, from the NAS to the router and network switch. Users must also ensure their cabling is appropriate for this configuration. Patience is key; testing may be necessary to achieve optimal performance.
In summary, while link aggregation may not drastically speed up transfers for an individual user, it dramatically improves the shared experience for multiple users accessing a NAS simultaneously. Families looking to enhance their home networks with this technology are likely to see immediate benefits, allowing for seamless media streaming and efficient backups without the bottlenecking that previously plagued shared setups.
What’s Next: As more users adopt link aggregation, further developments in home networking technology are anticipated. Families looking to optimize their NAS setups should consider this technology as a viable option for future-proofing their home networks.