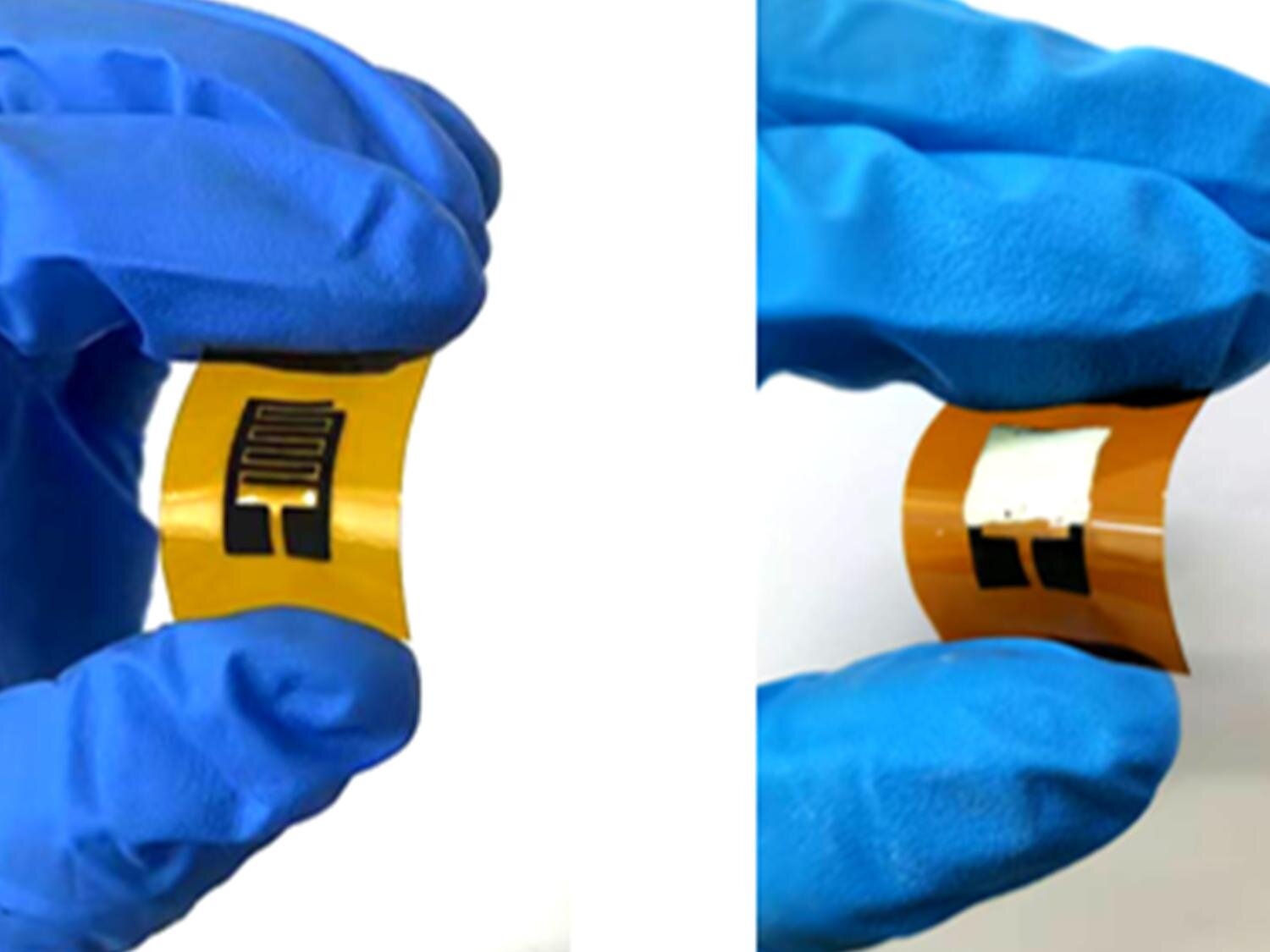
A team of researchers from the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) has developed a revolutionary breath sensor capable of diagnosing diabetes within minutes. This innovative device offers a non-invasive alternative to traditional blood tests, marking a significant advancement in diabetes detection.
The sensor operates by analyzing volatile organic compounds in exhaled breath. These compounds are indicative of metabolic changes associated with diabetes. In a study published in March 2024, researchers demonstrated that the sensor could accurately identify diabetes in participants with a high degree of reliability.
Breakthrough Technology in Diabetes Diagnosis
The development of this breath sensor is a substantial leap forward in diabetes healthcare. Currently, the standard procedure for diagnosing diabetes involves blood tests, which can be uncomfortable and time-consuming. In contrast, this new approach allows for a quick and painless diagnosis, enhancing accessibility for patients.
During the study, the sensor was tested on a diverse group of participants, leading to an accuracy rate of over 90% in detecting diabetes. This level of precision suggests that the breath test could be employed not only in clinical settings but also in home monitoring applications, making it easier for individuals to track their health.
Researchers have expressed optimism about the broader implications of this technology. The ability to quickly diagnose diabetes could facilitate earlier interventions, potentially reducing the risk of complications associated with the disease. Diabetes affects millions globally, with the World Health Organization estimating that approximately 422 million people are living with the condition.
Future of Diabetes Screening
The breath sensor’s development has garnered significant attention within the medical community. Leading experts emphasize that non-invasive diagnostic tools could transform diabetes management. According to findings reported by Medical Xpress, this technology is poised to play a crucial role in preventive healthcare.
The researchers at UCLA are exploring the potential of this sensor further. Future studies aim to refine the technology and expand its applications to include screening for other metabolic disorders. The ongoing research underscores the importance of innovation in addressing global health challenges.
As the project progresses, the team hopes to collaborate with healthcare providers and regulatory bodies to bring this technology to market. If successful, the breath sensor could become a standard diagnostic tool, ultimately improving the quality of life for those at risk of diabetes.
In summary, the introduction of a rapid breath sensor to diagnose diabetes marks a promising development in medical technology. With its potential for quick and accurate assessment, this innovation could reshape how diabetes is diagnosed and managed worldwide.