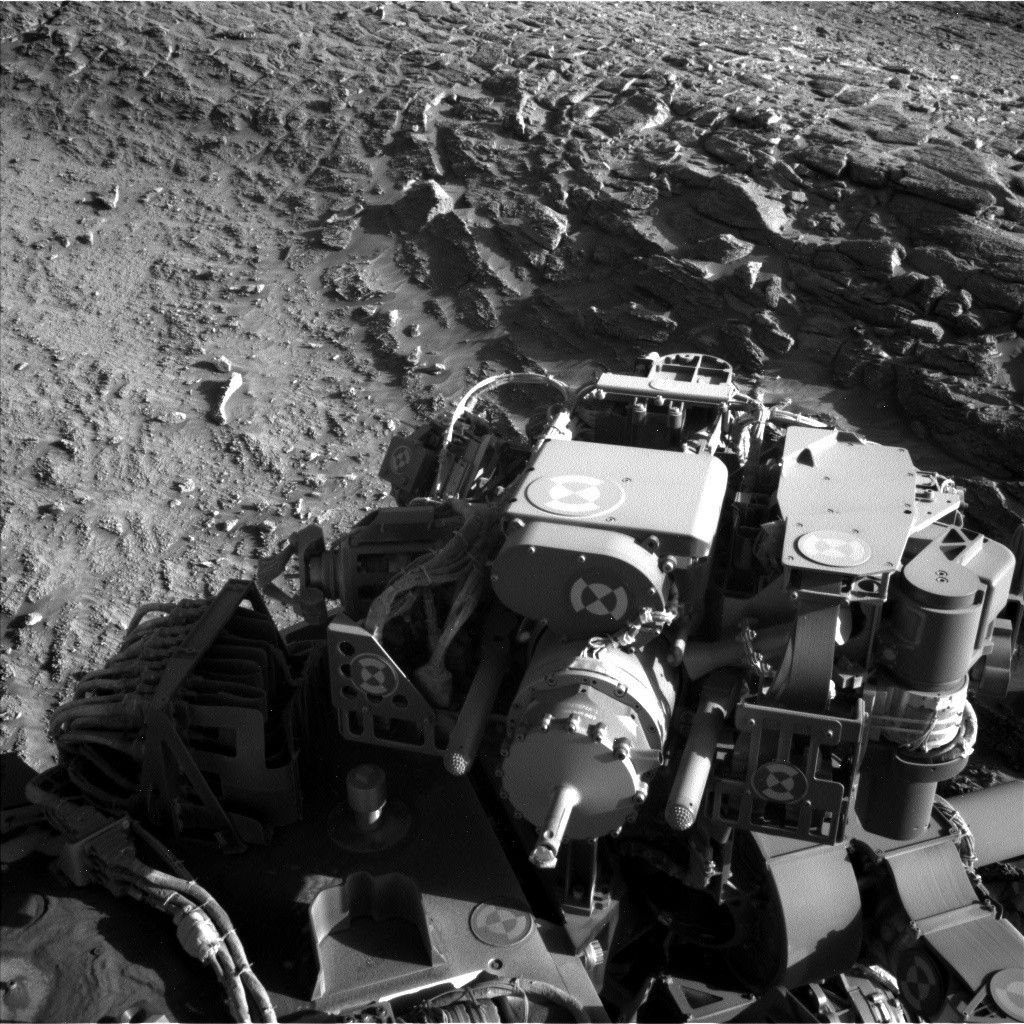
NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity has made significant observations while analyzing a geological feature known as “Río Frío.” On August 19, 2025, the rover captured images while parked against a fracture wall, marking Sol 4634, or the 4,634th Martian day of its mission. This exploration aims to uncover the internal structure and chemistry of the ridges that are prominent in the surrounding terrain.
Curiosity’s position against the Río Frío wall is not just a pause in its journey; it signifies a critical moment for scientific discovery. The rover’s team is focused on understanding why these ridges stand out compared to their surroundings. The observations taken along the wall will be instrumental in piecing together the geological history of the region.
Exploration Strategy and Scientific Tools
The exploration plan includes extensive imaging and analysis. Curiosity will utilize its Mastcam to create mosaics that cover the ridge from base to summit, providing a detailed view of the geological features. One of the targeted mosaic areas is named “Jardín de las Delicias,” where researchers anticipate uncovering a wealth of Martian geological information.
Additionally, the rover will employ the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) to analyze a nodule-filled area known as “Minimini,” and the SuperCam for examining a vein at a location dubbed “El Tapado.” These analyses aim to reveal the chemical composition of the materials found in the ridge.
Curiosity’s mission is supported by its other scientific instruments, including ChemCam imaging of the “Paniri” butte and additional observations with the Navigation Camera (Navcam) and Mastcam aimed at the sky. The rover’s Dynamic Albedo of Neutrons (DAN), Radiation Assessment Detector (RAD), and Rover Environmental Monitoring Station (REMS) will also be operational, monitoring the Martian environment throughout the exploration.
Future Endeavors and Ongoing Research
Following its work at Río Frío, Curiosity plans to drive towards a smaller ridge that runs perpendicular to the current feature. This new location promises further opportunities to delve into the secrets of Mars’ geological past. Each observation and analysis contributes to a broader understanding of the planet’s history and its potential for past life.
As Curiosity continues its journey, the insights gained from these investigations are expected to enhance our knowledge of Martian terrain and assist in the planning of future missions. The ongoing efforts by NASA’s team aim to piece together the intricate geological narrative of Mars, one exploration at a time.
For updates on Curiosity’s mission and to learn more about its scientific instruments, visit the official NASA website.